
C计划是一家致力于批判性思维教育的机构。C计划的C,是指Critical Thinking(批判性思维),Civic Education(公民教育)。推广思辨教育,重塑公共理性。
When the epidemic is approaching the city, is it discrimination to refuse tenants to enter the community?
Now is a critical period for the prevention and control of the new coronavirus pneumonia. Governments and residents have taken active and efficient measures to curb the epidemic, and these measures have played a significant role. However, we have observed that there are a variety of alleged discriminatory measures, which limit the legitimate rights and interests of some subjects by inappropriately discriminatory treatment. Discrimination not only affects the legitimacy and effectiveness of anti-epidemic measures, but also leaves a legacy of post-pandemic work, which should be reflected and corrected in a timely manner.

Three Discrimination Measures
Incomplete statistics of recent relevant media reports, the following measures are suspected of being discriminatory:
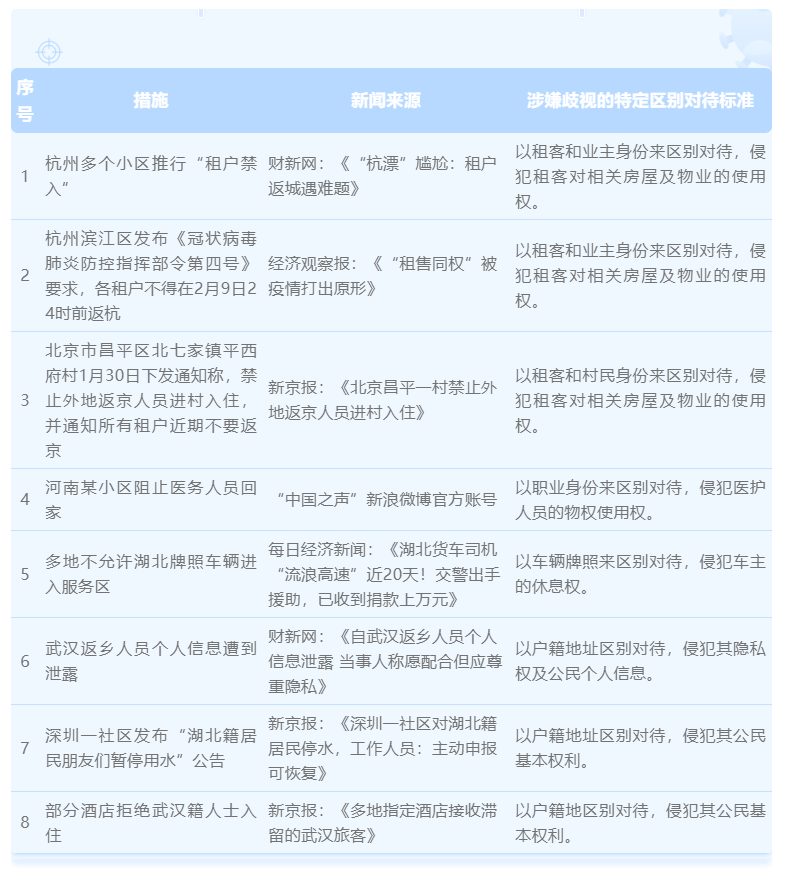
In general, the above-mentioned alleged discrimination measures can be roughly divided into three categories:
The first is to treat the tenant and the owner differently, infringing on the tenant's right to use the property rights to enter the community and use the related properties and facilities of the house;
The second is to treat the location of the household registration (especially Hubei or Wuhan household registration) differently, infringing on the legitimate rights and interests of citizens with relevant household registration;
The third is to treat them differently based on their occupational status (such as medical personnel), infringing upon the legitimate rights and interests of practitioners in specific occupations.


What is discrimination
Discrimination is a very tense concept. Although it is essentially a kind of differential treatment, the concept of discrimination in economics, sociology and law is very different due to different interests.
The legal concept of discrimination, which focuses on the negative evaluation of discriminatory behavior, aims to prohibit and regulate it. Some scholars define it as "any unreasonable measures prohibited by law against specific groups or individuals whose effect or purpose is to distinguish, exclude, restrict or preferentially treat fundamental rights". (Quoted from Zhou Wei: "Basic Constitutional Rights: Principles, Norms, and Applications", Law Press, 2006 edition)
According to He Xia, associate professor of the Law School of Southwestern University of Finance and Economics, in the book "Anti-Discrimination Law Lecture Notes: Text and Cases" edited by Liu Xiaonan, legal discrimination consists of the following five elements: differential treatment, areas prohibited by law , reasons prohibited by law, adverse consequences and causation .
1. Discrimination
Legislation, standards, measures and behaviors that differentiate, exclude or favor are all manifestations of differentiated treatment.
These differences in treatment may be reflected in laws and regulations, constituting institutional discrimination; they may also be embodied in specific practices, constituting behavioral discrimination.
2. Areas prohibited by law
In the fields of employment, social security, public education, access to public places, etc. involving the allocation of public resources, the laws of various countries prohibit discrimination in a relatively consistent manner. For example, the "Fair Housing Law" in the United States stipulates that homeowners shall not discriminate against tenants on the basis of race, religion, color, national origin, disability, gender and age.
3. Grounds for Discrimination Prohibited by Law
The two core international covenants, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights (signed but not yet ratified by China) and the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, provide for universal prohibition of discrimination—that is, on the basis of which characteristics are prohibited Discrimination. These characteristics include " race, colour, sex, language, religion, political or other opinion, national or social origin, property, birth or other status ".
At present, China does not have a unified legal definition of "discrimination" in domestic law, nor does it have a specific anti-discrimination law. The provisions on the prohibition of discrimination are mainly scattered in relevant legal norms, such as the Constitution, the Law on Regional Ethnic Autonomy, the Law on the Protection of Women's Rights and Interests, the Law on the Protection of the Rights and Interests of the Elderly, the Law on the Protection of Minors, the Law on the Protection of Disabled Persons, and the The Labor Law, the Employment Promotion Law and other laws expressly prohibit any discrimination based on ethnicity, religion, gender, age, disability, household registration , etc.
4. Adverse Consequences
Discrimination results in detrimental consequences for victims, such as loss of opportunities in education, employment, access to public services, derogation of rights, and mental damage.
5. Causation
Causation means that adverse consequences result from actions that are treated differently.
It is also important to note that not all discrimination is discrimination . The law prohibits discrimination while listing reasonable discrimination as an exception.
For example, the Convention on the Elimination of Discrimination in Employment and Occupation lists three situations that do not constitute discrimination:
One is differentiated treatment based on the inherent needs of a particular job;
Second , special measures for protection or assistance;
The third is differentiated treatment based on national security.
Article 16 of China's "Law on the Prevention and Treatment of Infectious Diseases" stipulates that "no unit or individual shall discriminate against patients with infectious diseases, pathogen carriers or suspected patients with infectious diseases", and it also clearly stipulates that before being cured or before the suspicion of infectious diseases is ruled out , the aforementioned subjects shall not engage in work that is prohibited by laws, administrative regulations and the health administrative department of the State Council, which is easy to spread the infectious disease .


How to judge whether differential treatment in epidemic prevention is discriminatory
This article believes that the following three-step method can be used to determine whether an act or measure constitutes “discrimination”:
1. Whether there is any specific differential treatment;
2. Whether the differential treatment infringes or restricts legitimate rights and interests;
3. Whether the differential treatment is prohibited, required or exempted by law.
Take the example of community managers prohibiting certain residents from entering the community.
Step 1: Is there any specific discrimination?
The community prohibits the entry of patients with new coronary pneumonia, Hubei nationals, tenants or medical personnel, all of which are based on specific standards to distinguish between the specific group and those outside the specific group-there are specific differences.

Step 2: Is it infringing?
This differential treatment restricts the legitimate rights and interests of specific residents such as the right to use the relevant houses and properties.
Step 3: Legal Prohibition or Exemption?
Some of this distinction is required by law and some is prohibited by law.
1) Reasonable distinction of legal immunity:
First of all, there is a legal basis for community managers to prohibit patients with new coronary pneumonia, virus carriers and suspected patients from entering the community.
Article 39 of the Law on the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases states that when a medical institution discovers a Class A infectious disease, it shall take the following measures in a timely manner:
(1) Patients and pathogen carriers shall be treated in isolation, and the period of isolation shall be determined according to the results of medical examinations;
(2) For suspected patients , separate isolation and treatment in designated places before diagnosis;
(3) For patients, pathogen carriers, and close contacts of suspected patients in medical institutions, medical observation and other necessary preventive measures shall be taken in designated places .
Those who refuse isolation treatment or leave the isolation treatment without authorization before the isolation period expires, the public security organ may assist the medical institution to take compulsory isolation treatment measures .
Article 41 of the Law stipulates that the local people's government at or above the county level may implement quarantine measures for persons in places where cases of Class A infectious diseases have occurred or in specific areas within the places, and report to the people's government at the next higher level at the same time. ; The higher-level people's government that receives the report shall immediately make a decision on whether to approve or not. If the people's government at a higher level makes a decision of disapproval, the people's government implementing the quarantine measures shall immediately lift the quarantine measures. During the quarantine period, the people's government implementing the quarantine measures shall provide living guarantees to the quarantined persons; if the quarantined persons have a work unit, the work unit shall not stop paying their work remuneration during the quarantine period. The lifting of quarantine measures shall be decided and announced by the original decision-making authority.
According to the Announcement No. 1 of 2020 of the National Health and Medical Commission, the new coronavirus pneumonia is a Class B infectious disease with Class A measures. Therefore, for patients with new coronary pneumonia, virus carriers and suspected patients who should be treated in isolation or take isolation measures according to the "Infectious Disease Prevention Law", community managers prohibit them from entering, which is a differentiated treatment permitted by law .

2) Discrimination prohibited by law:
It should be noted that patients with new coronary pneumonia, virus carriers and suspected patients are not equal to tenants, Hubei nationals or medical staff .
If the conditions of differentiated treatment are changed to tenants (property owner or property user), Hubei nationals (place of household registration) or medical staff (occupation), regardless of whether they are patients, suspected patients or close contacts, they belong to Restrictions or damage legitimate rights and interests with a specific distinction without legal immunity, and also violates the corresponding legal provisions .
It is true that people with certain identity characteristics - such as those who lived and traveled in Hubei after the outbreak, medical staff in the infectious disease department of the relevant hospital, etc. - do have a higher probability of being exposed to the virus, but here it is necessary to use a probability-based approach. There is an adequate balance between screening efficiency and civil rights.
On the one hand, it is necessary to consider the probability of people with these identities being exposed to the virus - for example, considering returning tenants as potential virus carriers, regardless of their specific signs or contact history; only looking at Hubei's place of origin and not Asking him whether he has a history of travel and residence in Hubei; just looking at the medical profession, regardless of whether his department may have contact with patients with new coronary pneumonia—this is a blind expansion of the object of exclusion. Such generalized criteria should not be used to discriminate between populations when more precise screening criteria are available (eg, their specific physical signs, travel history within 14 days, and exposure history).
On the other hand, even if people with certain identities do have a very high probability of infection, the exclusionary measures taken against them should comply with the principle of proportionality . Especially when such measures are carried out by public authorities, or by persons entrusted or authorized by public authorities to exercise public administration.
The so-called proportionality principle is to determine whether the restrictive behavior of public power is justified by weighing the means by which the public power restricts legitimate rights and interests and the purpose pursued by the restrictive behavior.
For example, for vehicles and drivers from Hubei, there is indeed a high probability of being exposed to the virus. The rest area of the expressway can designate a specific area for drivers to rest and avoid contact with others; however, simply and rudely refusing vehicle drivers to stop is not in line with the principle of proportionality .
For another example, close contacts can be required to be quarantined in a centralized manner or be quarantined at home for 14 days; however, if they install iron locks on their doorsteps, it is not necessary, does not comply with the principle of proportionality, and does not fall under the third category of the Law on the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases. "Other necessary precautions" stipulated in Article 19.

Correction
Some governments and relevant departments have noticed the discriminatory problem in the implementation of epidemic prevention measures, and have issued some documents to correct the deviation.
On February 7, 2020, the State Council’s Joint Prevention and Control Mechanism for Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia issued the “Notice on Doing a Good Job in Protecting Front-line Medical Staff and Their Families” (Pneumonia Mechanism Fa [2020] No. 23), “ Those who discriminate and isolate front-line medical staff and their family members should be criticized and educated in a timely manner, and if the circumstances are serious, corresponding punishment should be given.”
On February 9, the Central Network Information Office issued the "Notice on Doing a Good Job in Personal Information Protection and Using Big Data to Support Joint Prevention and Control Work", requiring that personal information collected during joint epidemic prevention and control should also refer to the "Personal Information Security Specification". Adhere to the principle of minimum scope, and the objects of collection are in principle limited to key groups such as confirmed persons, suspected persons, and close contacts, and generally do not target all groups in a specific area, so as to prevent the formation of de facto discrimination against groups in specific areas.
On February 10, the Hangzhou Epidemic Prevention and Control Headquarters issued the No. 34 requirement that rude methods such as locking doors and blocking passages should not be used to implement hard control of home isolation, and residents and tenants should not be arbitrarily restricted from entering the community. People and vehicles will be refused entry to Hangzhou on the grounds of license plate and foreign household registration.
On February 11, the Ministry of Public Security issued the "Notice on Effectively Doing a Good Job in Road Traffic Guarantee for the Prevention and Control of the New Coronary Pneumonia Epidemic". The "Notice" pointed out that for vehicles from other provinces or in key epidemic areas such as Hubei, but driving in different places for a long time, and not passing through key epidemic areas, except for necessary inspections such as epidemic prevention and temperature measurement of the people on the vehicle, no unauthorized restrictions shall be set. , persuade to return.
On February 11, 2020, the Standing Committee of the Shenzhen Municipal People's Congress issued the "Decision on Doing a Good Job in the Prevention and Control of the Current Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Epidemic and Effectively Protecting the People's Lives, Health and Safety", which stipulates that "No unit or individual may use the novel coronavirus to Rejecting and discriminating against people related to the epidemic on the grounds of pneumonia epidemic control.”
Even so, the discriminatory acts or measures discussed in this article still exist or occur repeatedly in many places. "Discrimination" may be an "epidemic" in another sense. This "epidemic" occurs based on panic and ignorance, and is also highly contagious and harmful. It violates the legitimate rights and interests of the discriminated object and detracts from its basic rights, violates their personal dignity, and discrimination from public power also damages the legitimacy and credibility of public power agencies. As part of a social community, I keep reminding myself that our enemy is the virus, not each other .

Note: The link to "News Source" in the table is as follows
Caixin.com: "The Embarrassment of "Hang Piao": Tenants encounter difficulties in returning to the city" link: http://companies.caixin.com/2020-02-12/101514400.html
Economic Observer: "Equal rights to rent and sell" are out of shape by the epidemic" link: http://www.eeo.com.cn/2020/0211/376048.shtml
The Beijing News: "Beijing Changping No. 1 Village Prohibits People Returning to Beijing from Entering the Village" link: https://news.sina.cn/gn/2020-01-30/detail-iimxxste7662758.d.html?vt=4&pos= 3
"Voice of China" Sina Weibo official account: https://m.weibo.cn/1699540307/4469452886441962
Daily Economic News: "Hubei truck drivers have been "wandering high-speed" for nearly 20 days! The traffic police helped, and donations of tens of thousands of yuan have been received" link: http://www.nbd.com.cn/articles/2020-02-08/1406565.html
Caixin.com: "Participant of Personal Information Leakage of Returnees from Wuhan Says Willing to Cooperate but Should Respect Privacy" link: http://china.caixin.com/2020-01-26/101508509.html
The Beijing News: "A community in Shenzhen shuts down water for Hubei residents, staff: Active declaration can be restored" link: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1657581867974388232&wfr=spider&for=pc
Beijing News: "Many designated hotels receive stranded Wuhan tourists" link: http://m.sohu.com/a/369177272_114988

author:
Xu Qianchuan practicing lawyer
Xian Yun trainee lawyer
▷ Edit: Blue Fang
▷ Typography: Yuxiang
Unless otherwise specified, the articles of Plan C are original. The signed illustrations and brain maps are also original. To reprint articles or original illustrations and brain maps, please contact Xiao C (WeChatID: Plan-C2016), or leave us a message.

Like my work?
Don't forget to support or like, so I know you are with me..
Comment…