
分享自己閱讀後的筆記與啟發,並期許自己像介白素(白血球之間用來互相傳遞訊息的分子)一樣,充當書本與讀者之間的橋樑。 歡迎大家指出文章中的謬誤,以及說出自己的看法。
Fund Management in Investing
To be successful in trading, traders must consolidate the three pillars of trading, namely money management, trading method, and trading psychology.
In my previous articles, I have talked about trading methodology (referring to the analysis and trading plan of the reasons behind buying and selling) and trading psychology (referring to emotion management and discipline).
Today, I will take you to a deeper understanding of money management.

money management
Before they don’t understand money management, most people probably only know “All in”, but if they do this, they are afraid that they will “sleep in the park” if they are not careful, or even “graduate” from the stock market.
So, we need to understand money management. Because money management allows us to manage risk and know how much money to put into a trade, it allows us to survive the stock market (avoid the risk of bankruptcy) and generate geometric profits (that is, the profit is much greater than from a single contract without money management the money you can earn) .
Note: It is important to note that bankruptcy risk is not necessarily a loss of the entire account balance, it may be a loss of 50%, 75% or 100% of the account, depending on your personal risk tolerance.
Place a stop
However, before introducing each money management strategy, it is necessary to recognize the stop loss, so that the maximum loss amount can be estimated.
There are two types of stop loss, quantitative stop loss and qualitative stop loss.
Quantitative stop loss is to use the amount of loss as a stop loss, such as setting a stop loss when a single stock loses 10% or a stop loss of 10% lower than the market price (ie moving stop loss method), and a stop loss when 10% of the total capital is lost.
Qualitative stop loss is the stop loss on the fundamental, technical and chip level, such as the original reason for buying disappears, a better target is found, and a technical sell signal appears (such as a break below the 60-day moving average or a certain support). price), a sell signal appears on the chip surface (for example, the shareholding ratio of large investors is less than 50%), etc.
anti-Martingale money management strategies
The “evening on dips” often heard is actually the Martingale fund management strategy.
This strategy assumes that after a losing trade, there is a higher chance of a profitable trade, and more trades should be added. But in fact, doing so increases the risk of bankruptcy, after all, no one can guarantee that you will not experience a series of losses.
Conversely, an anti-martingale money management strategy is the right strategy to help us survive because it trades less (decreased position size) when losing money and more (increased position size) when profitable .
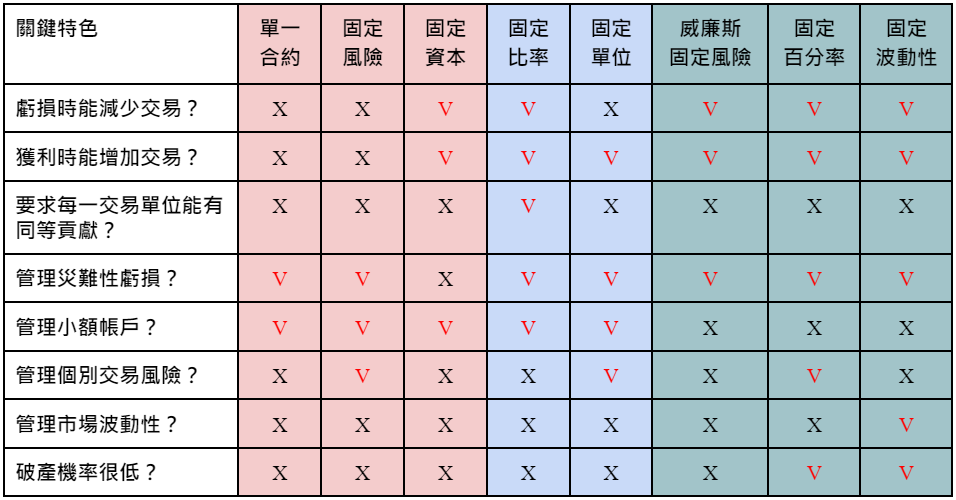
Next, we will use the Yuanta Taiwan High Dividend ETF (code: 0056, priced at 30,000 yuan) with a stock price of 30 yuan as an example, and predict that the maximum loss of 1 0056 stock is 4,000 yuan (down 4 yuan). One explores seven anti-martingale money management strategies (but some are not strictly speaking), namely fixed risk, fixed capital, fixed ratio, fixed unit, Williams fixed risk, fixed percentage, and fixed volatility.
As a comparison, when the initial account balance is 100,000 yuan, the single contract strategy, that is, when the fund management strategy is not used, can buy up to 3 0056 stocks.
1. Fixed risk
Fixed risk is limiting each trade to a fixed risk.
Fixed Amount Risk = Initial Account Balance/Number of Transactions.
Trading Unit = Fixed Risk/Individual Trading Risk.
Individual trade risk is the amount between the entry price and stop price plus commission.
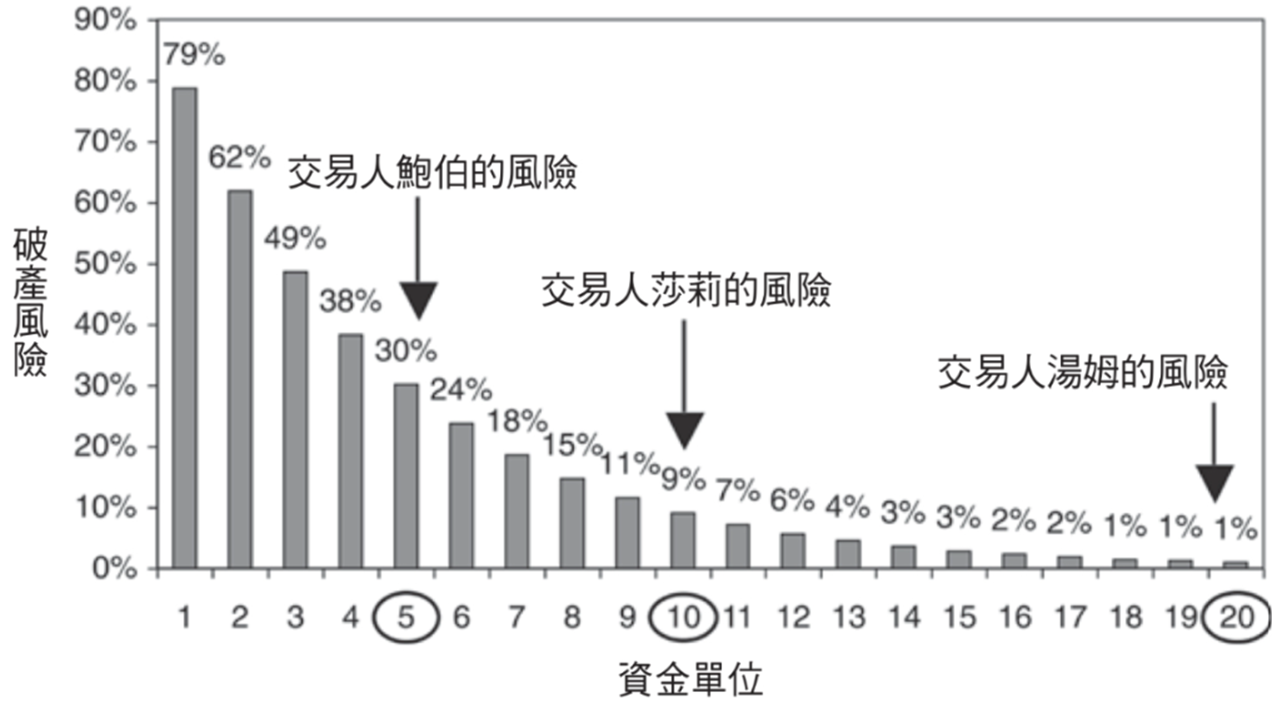
For the number of transactions, under the same conditions, the more transactions, the lower the bankruptcy risk. As shown in the figure below, the bankruptcy risk of Wubi is 30%, the bankruptcy risk of Ten is 9%, and the bankruptcy risk of 20 is less than 1%. Therefore, it is recommended to use more than 20 trades to reduce the bankruptcy risk to less than 1%.
Suppose you intend to use an account balance of 100,000 yuan for 20 trades, resulting in a fixed amount of risk of 5,000 yuan (100,000/20 = 5,000), so you only execute trades with an amount risk of 5,000 yuan or less. If the trading risk of a single stock is 4,000 yuan, you can only buy at most one 0056 stock per transaction (5000/4000=1.25, unconditionally round off the decimal).
However, the fixed risk strategy can't trade less when you're losing money, and you can't trade more when you're winning, because it expects you to risk a fixed $5,000 in these 20 trades at all times, but it at least Allow petty bourgeois to start trading.
Pros : Ability to handle catastrophic losses, small account availability, ability to manage individual trading risks.
Disadvantages : Can't reduce trades when losing money, can't increase trades when making a profit, can't require equal contribution from each traded unit, can't manage market volatility.
2. Fixed capital
Fixed capital is the exchange of one unit (eg one) of shares for a fixed unit of capital.
Trading Units = Account Balance / Fixed Capital Units per share.
Fixed Capital Units = Actual or Expected Maximum Loss/Risk Percentage.
Percentage blowtorch risk is the percentage of your account balance that you can lose with ease.
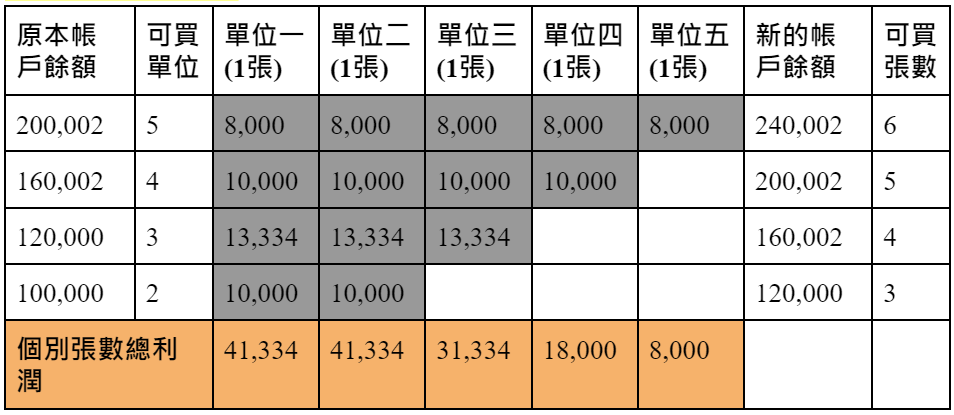
For example, when you can tolerate a 10% loss and estimate the maximum loss of a 0056 stock to be 4,000 yuan, the fixed capital unit is 40,000 yuan (4,000/0.1=40,000), and since your initial account balance is 100,000 yuan , so you can buy 2 0056 stocks (100,000/40,000=2.5, rounding off the decimals unconditionally).
The fixed capital strategy is one of the fastest strategies to increase the number of shares, because the more the number of shares, the less profit you need to make on each one to move to the next level. As shown in the table below, after the two 0056 stocks made a total of 10,000 yuan, the account balance became 120,000 yuan. At this point you are allowed to buy 3 stocks, so there are three stocks to reach the $40,000 target, so you only need to earn $13,334 per stock to get to the next level. This explains how fixed capital strategies can generate geometric profits.
However, even though a fixed capital strategy allows small accounts to grow quickly, it comes with a high level of risk, as it can result in large losses.
Advantages : Less trades when losing money, more trades when making a profit, available for small accounts.
Disadvantages : Inability to require equal contributions from each trading unit, inability to deal with catastrophic losses, inability to manage individual transaction risks, inability to manage market volatility.
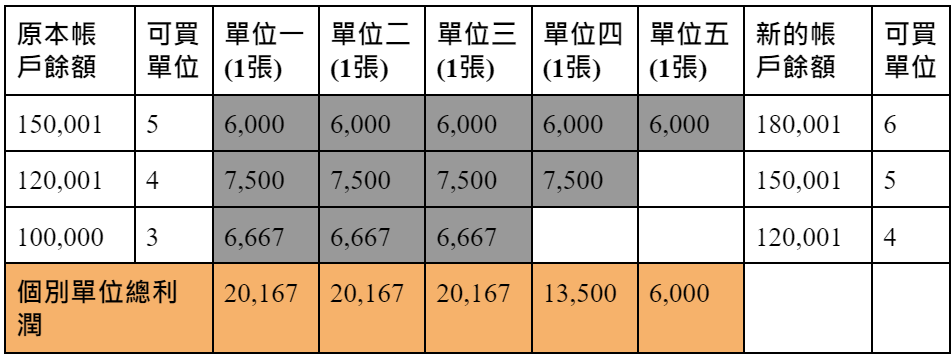
3. Fixed ratio
A fixed rate is a fixed rate delta (pronounced delta) to adjust the trading unit.
Next account level = current account level + (current number of shares × δ).
δ= maximum loss + initial margin.
Aggressive traders can use smaller deltas and conservative traders can use larger deltas.
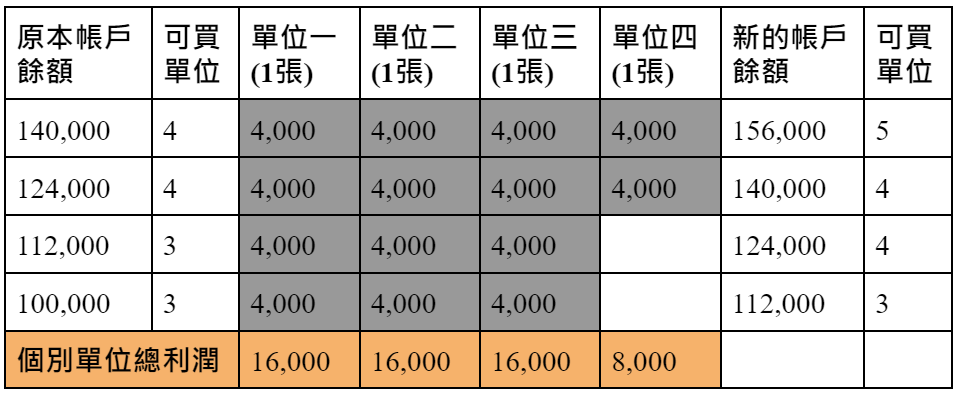
Although the fixed ratio strategy earns less profit than the fixed capital strategy, it still generates geometric profits and is far more capable of facing catastrophic losses than the fixed capital strategy because its requirement for equal contribution makes every unit Can absorb losses. As shown in the table below, assuming that the initial account balance is 100,000 yuan, the maximum loss of one 0056 stock is 4,000 yuan and no margin is required, the delta is 4,000 yuan, which means that before each trading unit can earn 4,000 yuan, you will Should not proceed to the next account level.
Advantages : Reduce trades when losing, increase trades when gaining, can require equal contribution from each traded unit, can deal with catastrophic losses (requiring equal contribution allows each unit to absorb losses), small account available .
Disadvantages : Inability to manage individual trading risks, inability to manage market volatility.
4. Fixed units
Fixed units are based on fixed risk, but the difference is that as your account balance increases, fixed units require you to risk more money, requiring you to recalculate your risk for each sum. so,
Amount risk per trade = higher account balance / number of trades.
Trading Unit = Fixed Risk/Individual Trading Risk.
The number of transactions is the same, it is recommended to use more than 20.
However, it doesn't reduce monetary risk when you lose money and your account balance drops, so it doesn't allow you to trade less when you're losing money and increase your bankruptcy risk. Therefore, if you believe that your strategy is robust and smooth, it is an aggressive strategy worth considering at 20+ trading units.
Another benefit of a fixed unit is its ability to differentiate risk between individual transactions. If a trade is too risky, it won't allow it.
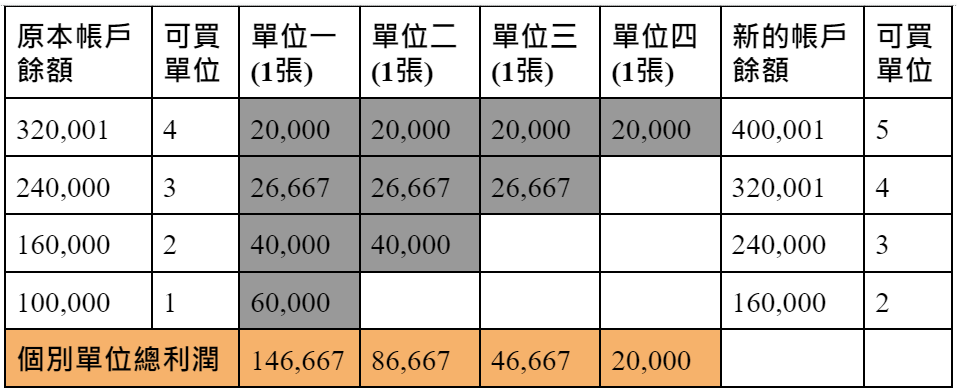
As with the fixed risk strategy, suppose you intend to use an account balance of 100,000 yuan for 20 trades, resulting in a fixed amount risk of 5,000 yuan (100,000/20 = 5,000), so you only execute the amount risk equal to or less than 5,000 yuan dollar transaction. If the trading risk of a single stock is 4,000 yuan, you can only buy at most one 0056 stock per transaction (5000/4000=1.25, unconditionally round off the decimal). But unlike the fixed risk strategy, once the account balance increases to 160,000 yuan, you can buy 2 0056 stocks (4,000×2=8,000, 8,000×20=160,000).
Advantages : Increased trading when profitable, ability to deal with catastrophic losses (equal contribution requirement allows each unit to absorb losses), small account availability, ability to manage individual trading risks.
Disadvantages : Inability to reduce trades in the event of losses, inability to require equal contribution from each traded unit, inability to manage market volatility.
5. Williams fixed risk
Williams fixed risk is somewhat similar to fixed capital.
Trading Unit = Amount Risk / Maximum Loss.
Amount Risk = Account Balance × Risk Percentage.
Risk percentage refers to the amount of trading account that will be lost in the event of a maximum loss.
When the account balance changes, the Williams fixed risk strategy needs to recalculate the amount risk of each trade, so when you make money, the amount risk will increase, and you can buy more units; when you lose money, the amount risk will decrease and need The number of units traded will drop.
Assuming that you have an account balance of 100,000 yuan and can tolerate a loss of 10%, the amount risk is 10,000 yuan (100,000 × 10% = 10,000), and the maximum loss of a 0056 stock is 4,000 yuan, then you can buy 2 0056 stocks (10,000/4,000=2.5, unconditionally round off decimals).
The Williams fixed risk strategy, like the fixed capital strategy, is one of the fastest strategies to increase the number of shares, because the more the number of shares, the less profit you need to make on each one to move to the next level.
In addition, the Williams fixed risk strategy can handle catastrophic losses with ease, but it is not suitable for small investors.
Advantages : Reduce trades when you lose, increase trades when you gain, can deal with catastrophic losses (can make up for losses with trades faster).
Disadvantages : Unable to require equal contribution per trading unit, not suitable for small accounts (unless the maximum loss is quite small or the risk percentage is high), cannot manage individual trade risk, cannot manage market volatility.
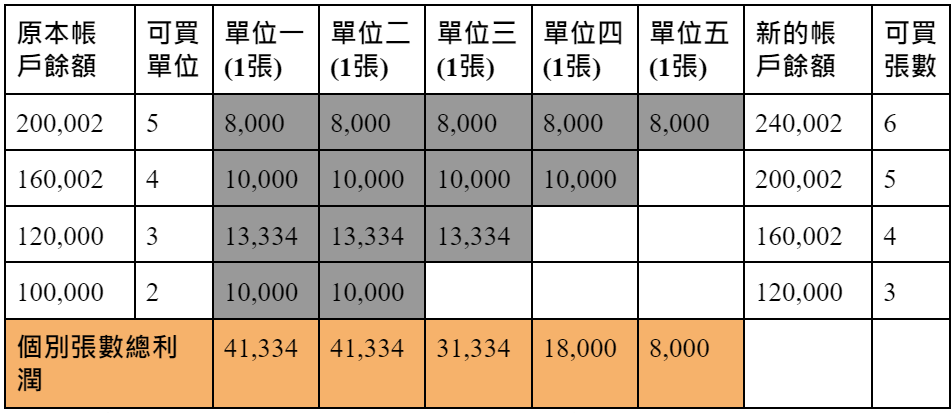
6. Fixed percentage
A fixed percentage is the most common money management strategy used by professional traders, which limits losses to a certain percentage of the account balance.
Trading Unit = (Fixed Percentage × Account Balance)/Individual Trading Risk.
The fixed percentage strategy is most commonly used by professional traders because it reduces the risk of bankruptcy very effectively. When the fixed percentage is 5%, it takes 104 consecutive losses to go bankrupt; when the fixed percentage is 2%, it takes 263 consecutive losses to go bankrupt; when the fixed percentage is 1%, it takes 528 consecutive losses will go bankrupt. Therefore, a fixed percentage = 2% is most often chosen .
If you have an account balance of 100,000 yuan and face a trading risk of 4,000 yuan for a single stock, and want to limit the risk to 2% of the account, then you cannot buy a single 0056 stock ((100000×0.02)/4000 =0.5, round off the decimal unconditionally); but if you have an account balance of 300,000 yuan, you can buy one ((300000×0.02)/4000=1.5, round off the decimal unconditionally).
A fixed percentage strategy also achieves the goal of money management, allowing you to increase trading units when you are making money, and constrain you to decrease trading units when you are losing money.
A fixed percentage strategy also achieves the goal of money management, allowing you to increase trading units when you are making money, and constrain you to decrease trading units when you are losing money.
Advantages : Reduce trades when you lose, increase trades when you gain, deal with catastrophic losses (extremely effective in reducing bankruptcy risk), manage individual trade risk (limit exposure through fixed percentages).
Disadvantages : Unable to require equal contribution per trading unit, very unsuitable for small accounts (difficult to find trades risky enough to trade), unable to manage market volatility.
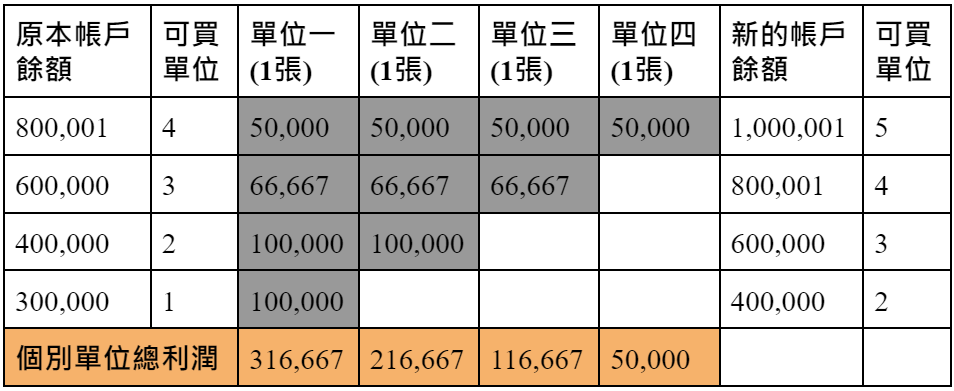
7. Fixed volatility
Fixed volatility is also known as fixed percentage volatility because it is a fixed percentage that limits market volatility to account balances.
Trading Units = (Fixed Percentage × Account Balance) / Market Volatility.
Market volatility refers to the fluctuation of stock prices during a specific period, which may be the average of the daily fluctuation range of 10, 20, and 30 days. It is best to adjust the duration of the volatility to be consistent with the trading time structure , such as short-term trading. The unit of person is the day, and the unit of long-term trader is the unit of month.
Assuming that the 20-day average stock price volatility of 0056 is 0.6 yuan, the account balance is 100,000 yuan, and you want to limit the volatility to 2%, then you can buy three 0056 stocks ((100000×0.02)/(0.6×1000 )=3.3, unconditionally round off decimals).
The biggest feature of fixed volatility strategies is managing market volatility. When markets are choppy and volatility spikes, trade units fall; when markets calm down and volatility decreases, trade units increase. However, if the market volatility is within the fixed percentage limit, you still have to take all the signals, so the fixed volatility strategy cannot manage the individual risk of the trade.
Advantages : Reduce trades when losing, increase trades when profitable, deal with catastrophic losses (effectively reduce bankruptcy risk), manage market volatility.
Disadvantages : Unable to require equal contribution from each trade unit, Not suitable for small accounts (harder to find stocks with low volatility), Unable to manage individual trade risk (if market volatility is within a fixed percentage limit, you still have to take all signals) .
Summarize
First of all, the fixed risk strategy must be eliminated , as it can neither reduce trades on losses nor increase trades on profits, and even generate less profit than a single contract! Next, remove the fixed capital strategy , because while it can accrue trading units quickly by contributing minimal profit per trading unit, it also makes it very difficult to deal with catastrophic losses.
If you are a small trader and your account is only 10,000 or 20,000 yuan, you will find that it is difficult for you to use Williams fixed risk, fixed percentage, and fixed volatility strategies to trade, so you only have fixed ratio and fixed unit strategies to choose from. At this time, it is advisable to choose a fixed ratio because fixed units cannot reduce trades when losing money, and fixed ratios suffer less from catastrophic losses.
However, there is also a common situation in the stock market - "a series of losses" that has not been accounted for, and fixed ratios are unlikely to cope with this situation. So, once you have enough balance in your account, you can choose three other strategies to reduce the risk of bankruptcy. Of the three, fixed percentages are the most likely to reduce bankruptcy risk, which is why professional traders prefer fixed percentage strategies .
In the end, since everyone's account size, risk tolerance, and trading ability are different, choose your own preferred money management strategy .
In addition, I will attach Brent Penfold's book "Trading Bible" to compare the results of these money management strategies through his set of currency futures trading methods called Forex_Trader for your reference.
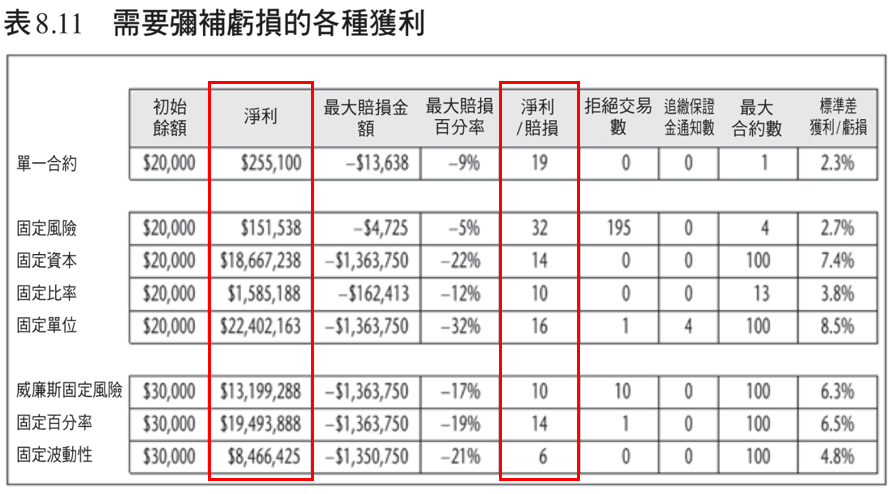
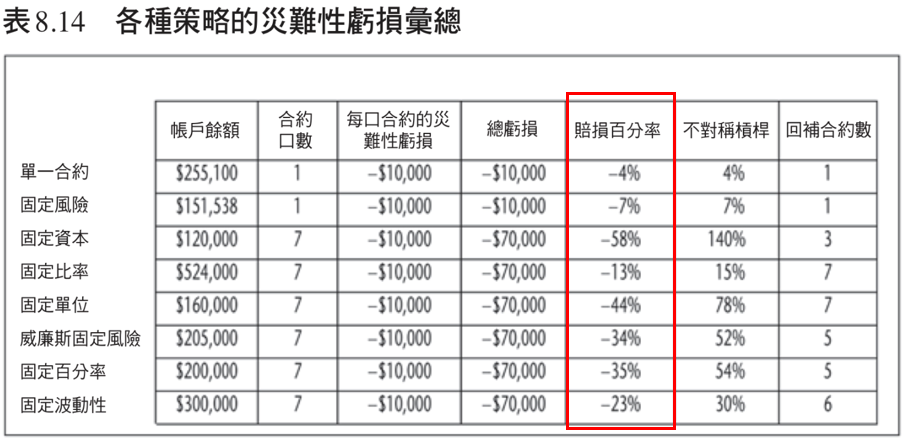
References
(1) Brent Penfold. (2019). The Trading Bible: Six Rules for Winning Trading, Building a Winning Model for Consistent Profits (Second Edition). Big name publishing.
(2) The stock market hermit. (2022). Hidden market to get rich map: 6 billion traders use a map to find the winning stocks that have risen by more than 30%. The big one is culture.
Like my work?
Don't forget to support or like, so I know you are with me..
Comment…