The Cancelled Future: The MiniDisc You Missed And Didn't Miss
This article was first published in " BIE Else ", and here is the original manuscript before editorial changes. For reprinting matters, please contact " BIE Others ", unauthorized reprinting is prohibited.
What is a "cancelled future"?
"Cancellation of the Future" is a theory put forward by the late cultural theorist Mark Fisher in the late 2000s, roughly saying that since the beginning of the 21st century, human cultural development has Things get into a bottleneck due to excessive borrowing intentionally or unintentionally, and cannot make a qualitative breakthrough in "creating the future" like in the past.
Looking at the cultural "new things" around us now, it seems that this is really the case. Except for the failure of rock music, the old movies, old TV and old games will either be restarted, or the sequel of the eighteenth generation will change the soup without changing the medicine. After all This is the safest for investors. When the 40- and 14-year-olds around you are playing the same Pokémon and skin-changing MOBA mobile games, it may be useless to pursue an unexpected future. No matter what.
What would the "cancelled future" look like if it were a physical item?
It's too cryptic to go further, let's talk about reality. If the "cancelled future" were a physical object, what would it look like? I think first of all, it should look very next-generation in appearance, very futuristic, but at the same time, some people think it is very retro, showing the conflict between the future and the past; functionally, it was designed to be a human in the future service, but it failed to become a common item in the future world. From this point of view, if the "cancelled future" can correspond to a physical item, one of its appearances is likely to be like this:

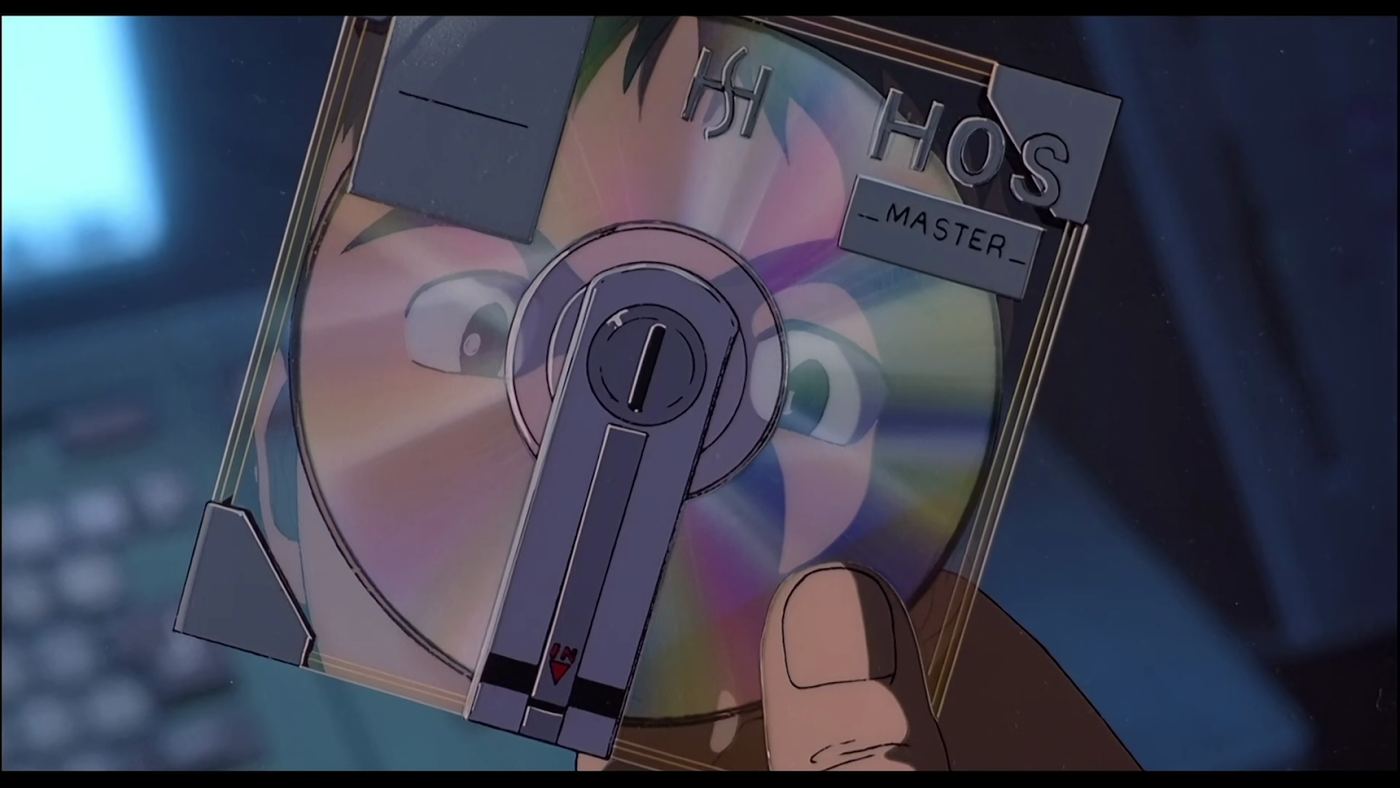
Maybe you will ask: "Student, how did you put the CD into the 3D printed save key?"
This isn't a spoofed save key, or an imprisoned CD, but a "next-generation" music storage medium that was once all the rage in some parts of the planet and nonexistent in others: MiniDisc CD, hereinafter referred to as MD).
MiniDisc: Since 1992
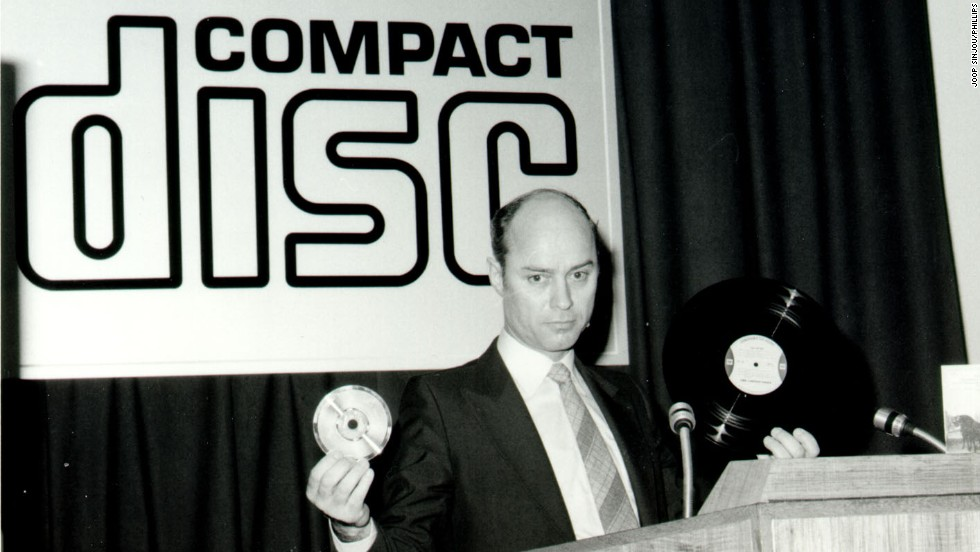
Since Philips and SONY jointly launched CD (Compact Disc) as a music storage medium in 1982, listening to high-fidelity music anytime and anywhere has become no longer an illusion. CD music surpassed vinyl records in sales shortly after its release, and overtook tape music in the early 1990s as the most popular high-fidelity music medium on the market.

However, people who were accustomed to recording songs (piracy) and listening to songs on tapes at that time also quickly discovered the shortcomings of CDs: the discs were too brittle and could not help tossing; although the sound quality was good, the portable CD players were too bulky, and when walking Too bumpy and skipping; can't record songs on it... In general, CDs are too squeamish, too guarded, not punk enough to shock the system.
Inventors were naturally aware of the inadequacies of CDs and began to develop the next generation of music media on the basis of CDs shortly after they were released. Faced with the shortcomings of CDs, people in the mid-1980s developed magneto-optical discs that were smaller in size and could repeatedly rewrite data.
After the birth of the magneto-optical disk, it has been widely used in the computer industry in Japan, but it is insufficient in other places. In the 1980s, Western society's doubts, fears, and longing for Japan were often expressed in the novels and movies of the 1980s. The image of Japan at that time influenced the vision of the future in the Western world, so that magneto-optical discs frequently appeared in Hollywood movies in the 1990s, appearing in the image of "spyware" items, and became a gimmick product that shaped the atmosphere of the movie.

Ten years after the birth of CD, SONY launched the next generation of mature music storage medium: MiniDisc on the basis of magneto-optical disc in 1992.

The culmination of tapes and CDs
MD is a genuine combination of tape and CD. It has the ability to rewrite and rewrite many times and durable casing of tape, and at the same time, it has the data storage method and shiny surface of CD: when playing disc, MD is exactly the same as CD. , use the laser to read the data on the disc surface; when recording music, the laser head heats the disc surface to activate the magnetic medium on the disc surface, and the data on the disc surface is changed by the writing head to complete the recording.

The default playback time of an MD disc varies from 60 to 80 minutes, which is about the same as a CD (with a low bit rate, it can be delayed by two to four times). The magneto-optical disc feature of the MD makes it easy to record, and it can also be used to rip music from other sources to create a mixtape.
MD uses the ATRAC data format developed by SONY itself. Although it is a lossy format (292kbps) compared to CD and WAV files, the sound quality is good enough that most people cannot hear the difference. In the early 1990s when recordable discs (CD-Rs) were expensive, being able to record digital music files at a more affordable price was undoubtedly the biggest selling point of MDs.
The compact size of the MD disc is another selling point. Its diameter is much smaller than that of a CD, and its thickness is only half that of a magnetic tape, which provides a prerequisite for a new generation of portable music players to debut in a smaller size.

In terms of product aesthetics, the protective casing of the disc can make the MD play more tricks in the appearance design like a magnetic tape, and also make the MD disc more suitable for playing. Loading music with MDs of different colors seems to add different filters to the music, and adjust the EQ for your music subconsciously.

Although MD is quite cool as a storage medium, the hasty debut of the first MD player failed to give MD a good start.
MD Player: From Bloated to Gorgeous

The SONY MD Walkman MZ-1, launched in late 1992, was the world's first MD player. The success of the tape Walkman has made SONY aware of the importance of on-the-go listening to songs, so this first player was striving for portability, but it failed to achieve the same success as the first tape Walkman. Although it continues the name of the Walkman, the portability is quite worrying. It is much larger than the Walkman in the early 1980s (114 x 139 x 43mm, 700g). It is still a bit difficult to insert it into a pocket.

What's more outrageous is that the internal battery is only enough to play 75 minutes of music, and it can barely finish playing a single disc. If your hands are not honest and switch songs back and forth, it is estimated that after half a disc is played, the fire will be turned off. It is said that SONY only sold less than 50,000 machines in the first year after MD's first player went on the market.
In terms of "software", self-recording MDs have not yet become popular, and the dirty and fast tape ripping is deeply rooted, and it is still an irreplaceable music sharing method. Compared with the tapes and CD albums of the same period, there are very few commercial music albums released on MD discs (although there are many blockbuster works), and most of them are works by musicians under SONY's own music label.


After all, it is a new medium that has been carefully researched for many years, and SONY will naturally not give up because of the initial failure. In the years following the unsatisfactory first machine, a series of MD revamps immediately followed.
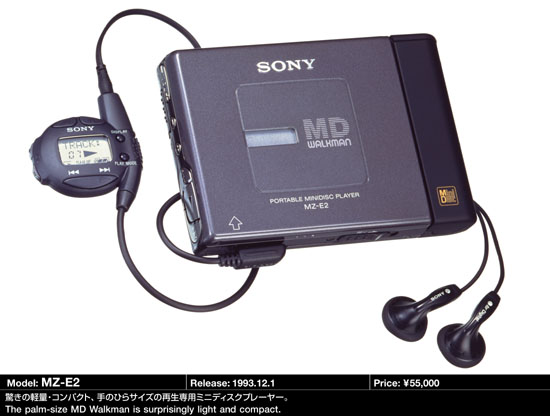
The MZ-E2, which was launched at the end of 1993, removed the recording function and only appeared in the form of a player. Compared to the first phone, the E2 is very compact (106 x 76 x 19mm) and weighs only 220g. The built-in battery can play for two hours, and the external battery box can reach 4 hours. It can already be regarded as a pocket machine that can be taken out.

Not long after, MD desks like tape decks and home CD players were launched, with the intention of making the MD part of a home Hi-Fi audio kit. In the development of portable MD players, the further miniaturization of the size, the enhancement and improvement of functions, and the diversification of the design of the fuselage made the presence of the MD gradually enhanced in the second half of the 1990s. At the same time, AIWA, SHARP, Panasonic, Sanyo, Kenwood and other audio and electrical product companies you can think of have also joined the production of MD players.
The MZ-R30 and R50, which were launched in 1996 and 1997 respectively, are two classic models of MD players. While not the flashiest machines, they're pretty much the MD's inflection point for bloat and low battery. Both machines are full-featured models that can record and play, but they continue the miniaturization of the MZ-E2 in terms of volume and weight, and the built-in battery can play for up to 7 hours. Models born after it tend to be more power efficient, with dozens of hours of playback on a single AA battery.


Portable MD players are further miniaturized. Due to the size limitation of the music medium, the thinnest and lightest tape Walkman cannot compete with the MD in terms of portability. The MD has become the easiest portable music player to carry.
The model diversification process of the tape Walkman in the past 20 years also happened to the MD player, but it was compressed in just a few years, which led to the explosive eruption of the design of the MD player. In addition to the black and black classic business-style design of the early models, the design style called "Y2K" in retrospect, accompanied by the consumerism frenzy in the Western world, played a big role in the design of MD players: shiny chrome , transparent plastic discs, pseudo-3D rendering dimensional breakthrough shells and other elements full of the times are all available, and a carnival at the end of the century will be carried out before the iPod brings the trend of minimalism.
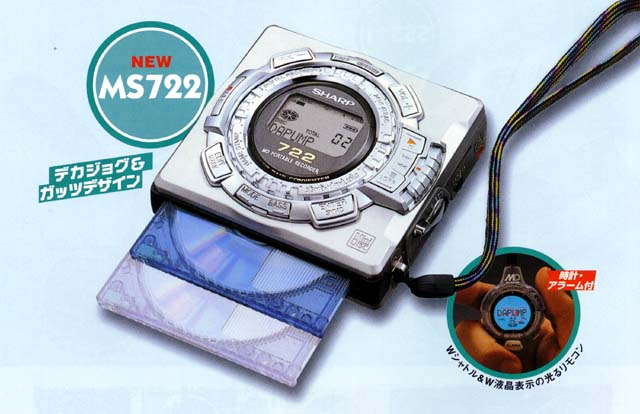
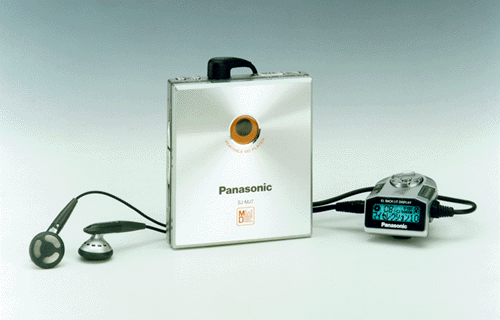







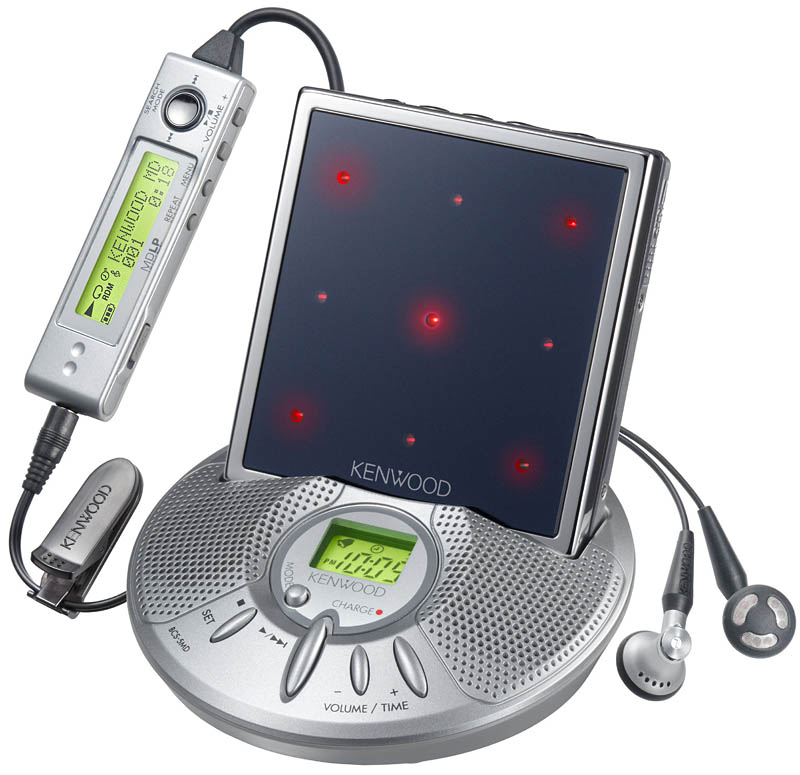


At the beginning of the Internet era, MD lost contact
In the late 1990s, with the proliferation of various models of MD players, more commercial music albums began to be released on MD, and MD, the music medium, finally gained a strong presence in developed regions in Asia and some European countries. Most countries in the world have little interest in MD because of SONY's limitations in market development. Because the popularity is not high, MD looks sci-fi enough and is often used by Hollywood to fool people.


In the real world at this time, due to the advancement of technology, the price of recordable CD-Rs has plummeted, and it is already a feasible way to burn CDs at home. More importantly, with the increasing popularity of the Internet, MP3 music began to change the way people listen and share music. In contrast, MD is quite old, and still needs to complete real-time recording like operating traditional audio equipment. As a digital file player, it has not been able to connect it with a computer to enjoy the convenience of digital equipment.
Faced with this criticism, in December 2001, two months after Apple's first-generation iPod went on sale, SONY finally belatedly released the Net MD series of MD players that can be connected to a computer with a data cable.
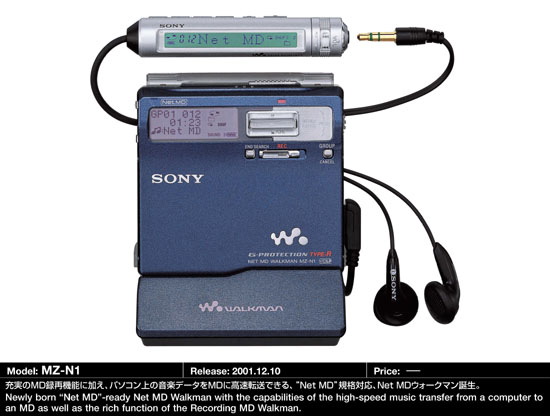

Net MD series players can convert various music formats into ATRAC format and copy them to MD discs. The speed is much faster than real-time recording, and it is more convenient to arrange playlists on the computer.
Unfortunately, although there is a "Net" in the name, the interconnectivity between Net MD and the Internet has nothing in common. Writing is one-way, and music can only be copied from the computer to the MD player through SONY's exclusive software. That is to say, you can't copy the songs from your friend's MD disc to the computer in reverse as you can with a U disk and an MP3 player, unless you use the MD for traditional audio input to the computer and wait for a long 70 minutes , and then manually split the track, rename, archive... etc., and this can be done with ordinary MD. This design was incredibly backward at a time when the creation of CD ISO images was mature.
Even more frightening is that Net MD's matching transfer software can only allow one music file to exist on three discs at the same time. If you want to write the song to a new disc, you must erase it from a previously written disc. These restrictions due to copyright protection made MD unable to meet the pursuit of open source, sharing and other next-generation lifestyles in the early days of the Internet when MP3 file download and sharing had become increasingly popular.
If Net MD can be launched a year earlier than it actually is, and the files can be transferred freely, there is no restriction on file formats, and there is room for users to make full use of the street-smart of the digital age, maybe MD will be more popular in the 2000s... ...of course, that's just what if.
Hi MD! Goodbye MD!
In 2004, the iPod is about to enter the fourth generation, and the average MP3 player is already cabbage price. There are few CD players on the market that dare not have the MP3 playback function. The MD is obviously gone. SONY made the final upgrade to the MD series before fully switching to MP3 players: Hi-MD.
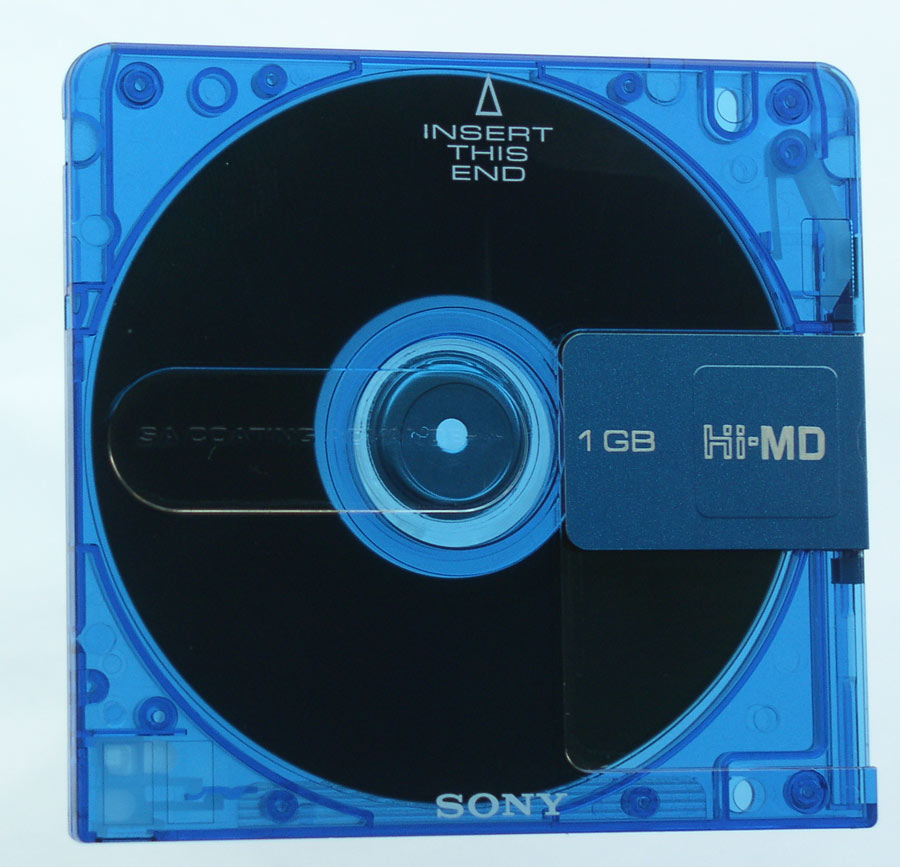

Hi-MD uses a new Hi-MD disc with a capacity of 1GB, which provides the ability to play lossless music, but still does not support file transfer from the disc to the computer. In the country of portable Hi-MD players, only SONY is left behind, and other manufacturers have already abandoned their ships.
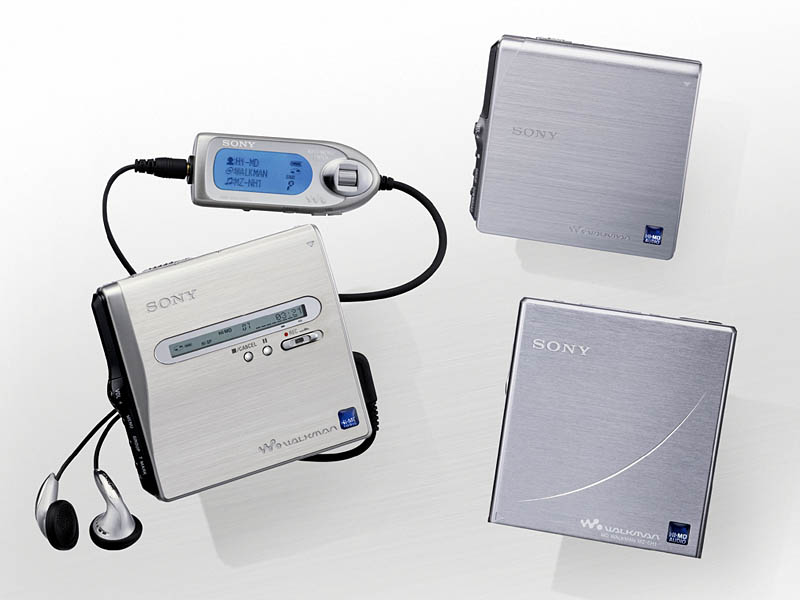
In 2006, SONY launched the MZ-RH1, the ultimate model of Hi-MD, which was also the last portable MD player launched by SONY. This is a full-featured machine that can record and play, but is only a little bigger than an MD disc. The materials used are high-end, the appearance is beautiful, and it is full of technology. It can be regarded as a good ending for MD. In addition, this is the only MD player that can copy the contents of MD discs to the computer, but by this time no one cares.
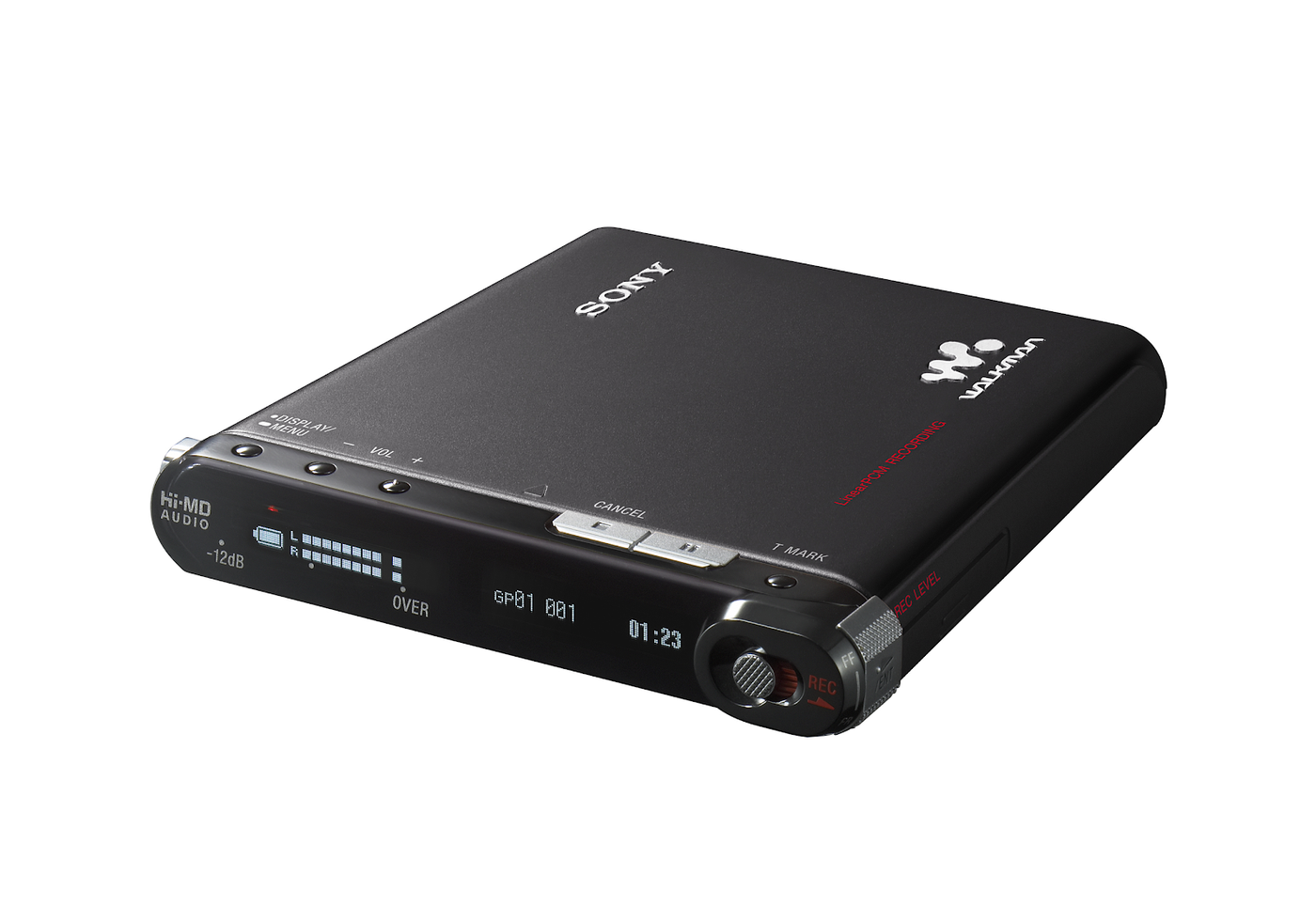
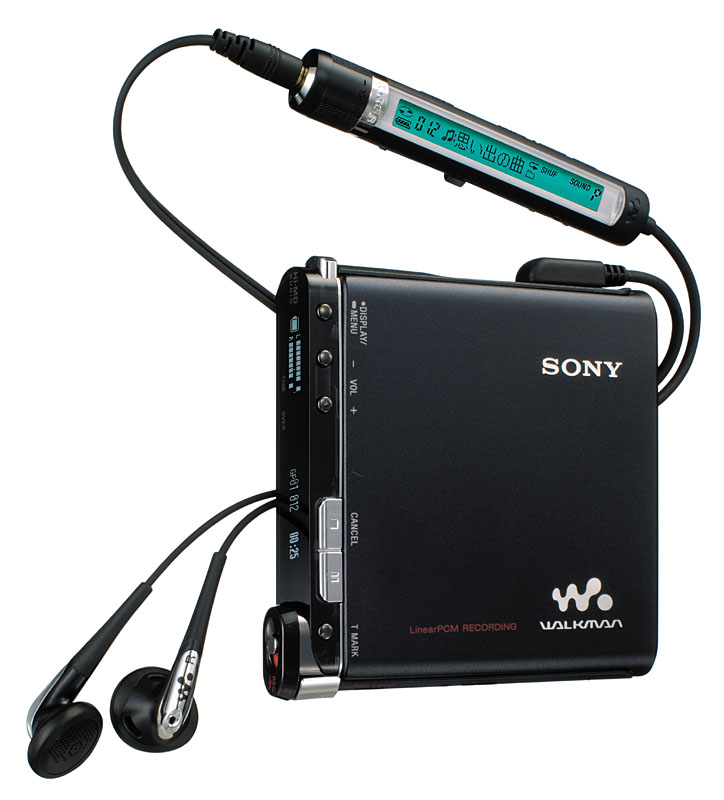



After this machine, SONY never launched a new MD model, to concentrate on MP3 players, the self-created ATRAC digital music format was not open source until death. In fact, SONY has launched a digital player using flash memory as early as 1999, but it can only play its exclusive ATRAC format, which is too arrogant. Unfortunately, at that time, both manufacturers and users favored MP3s that were close to the people. It was not until the end of 2004 that SONY launched a player that can directly play MP3 files for the first time.
On the Museum of Ancient Media , it can be seen that "MiniDisc was born in 1992 and died in 2013".

This is because SONY announced the discontinuation of all MD players in 2013. The announcement at the time was surprising, as many thought MD had died many years ago, but no one could say exactly when: some said it might have been after two fewer restaurants. When I could buy a flash MP3 player; some say it was when the color-screen iPod came along; some say it was when Spotify was still playing pirated music.
But, is MD really dead?
Search, and today you can still see independent musicians struggling to find MD discs with transparent shells, and then printing custom patterns on them to physically disseminate their music; there are also technologists who are studying how to use the WIN10 system. Running Net MD's supporting transmission software, how to make the driver of the MD player run normally on the new system; in addition, perhaps inspired by the Cassette Store Day, this year, someone organized the first " MiniDisc Day " online to help independent musicians promote Post copies of works for sale on MD.
Of course, those who are still silently listening to music with MD are not to be missed.

On the other hand, MD has also become a less popular cultural label. In 2018, Kanye West used the photo of MD as the cover for the unlisted new album; there are also users on Tumblr who spontaneously made MD mock-ups for their favorite entertainment products. Since it is no longer possible to pursue the latest electronic products to highlight personalized fashion tastes (because you have others, and they are half a beat faster than you), so go back and chase the ones born in the past, but not so people. known product.

In a big way, MD had an advanced concept when it was born, and it was difficult to wait until the era when it should be released and worked hard, but it was too restrained and cut off its future; MD was born in the same company and produced in the same year. The same function of the product In an era when there were more than a dozen optional models in different shapes, it had a cool look that edgy teenagers, digital enthusiasts, and trendsetters could not stop, allowing product designers to turn digital products into all ages in a minimalist and flat style The generic look was completely addictive before.
To put it mildly, MD used to be a music listening tool loved by some people, a high-end digital product that some people only heard about, and a gimmick product that some people have never heard of, and now they don’t believe it. fog pieces.
You missed it and you didn't miss it.
What MD represents is the future we have not been able to enter that the future weavers have worked hard to weave in the past.
Poppel Yang
2020-12-16
Like my work? Don't forget to support and clap, let me know that you are with me on the road of creation. Keep this enthusiasm together!





