
https://linktr.ee/penfarming 金融職人|文案編輯|雜食性閱讀者|Heptabase 愛用者 🌐 區塊鏈科普網站【鏈習生】專欄作家 🗞️ 電子報【創作者經濟IMO】主編 👤 臉書專頁【閱讀筆耕】
Reading pen farming | What is impermanent loss? Pay attention to providing liquidity
Recently, many people have been mining liquidity on the OSMOSIS exchange, which is accompanied by a term called " Impermanent Loss ". This article will try to explain it clearly.
■ Start with CEX and DEX
If you have experience in exchanging LikeCoins for fiat currency, the place for "pending orders" is the Centralized Exchange ( CEX ), where the price is matched by buyers and sellers and determined by market forces .
In contrast, Decentralized Exchange ( DEX ), where everyone can initiate market creation, in detail, is to create a coin pool (creat new pool), which contains two cryptocurrencies, which constitute A group of trading pairs; others are not idle, they pour water and invest in their two cryptocurrencies to increase the liquidity of the pool, so they get rewarded, which is called yield farming.
Trading on the DEX is very interesting, it is connected to the wallet, plug and play, and there is an interface that is very similar to a vending machine, allowing you to use currency exchange (swap). The question is, how is the quotation here?
The answer is through smart contract matching, given a mathematical model, the price is determined by the number of cryptocurrencies in the pool , which is called Automatic Market Maker ( AMM ).
So the conclusion is that the "price decision" in CEX and DEX has different systems.
■ The beginning of the story
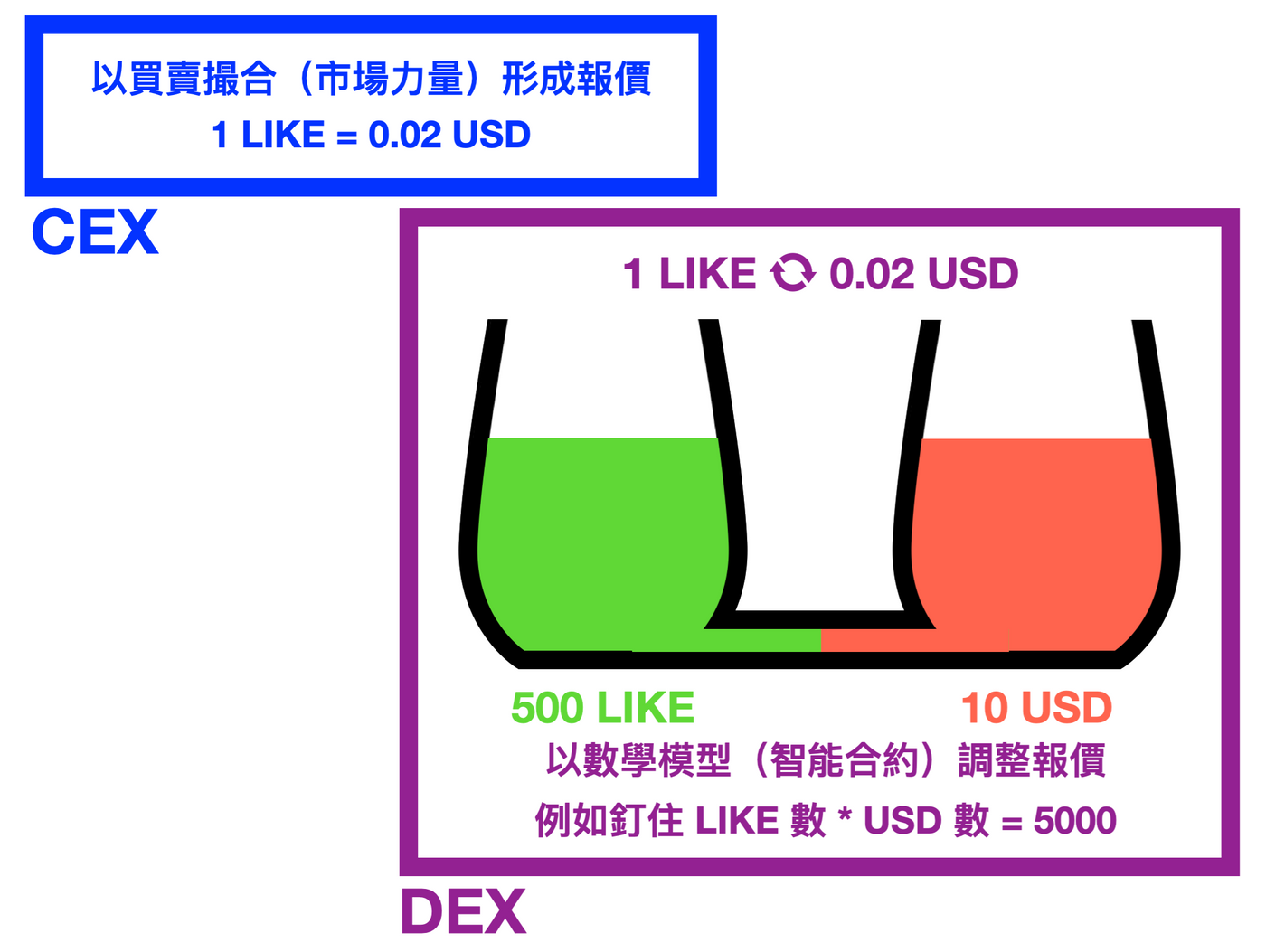
Suppose there is a set of cryptocurrency trading pair LIKE/USD, the price on both exchanges (CEX and DEX) is 1 LIKE = 0.02 USD; take out 1000 LIKE, put this set of trading pairs in the DEX currency pool, so put The principal is split in half and split into 500 LIKE and 10 USD….
Fang Caiduan mentioned that DEX uses smart contracts (mathematical models) to adjust the quotation . It is assumed that there is a relationship behind the “multiplication of the two coins, and a fixed value must be pinned”, that is, the number of LIKEs * the number of USD = 5000.
The values in the example are not important themselves, they are just to facilitate the introduction of concepts and make them concrete. The schematic diagram is as follows⇩:
■ Feel the dynamic adjustment first
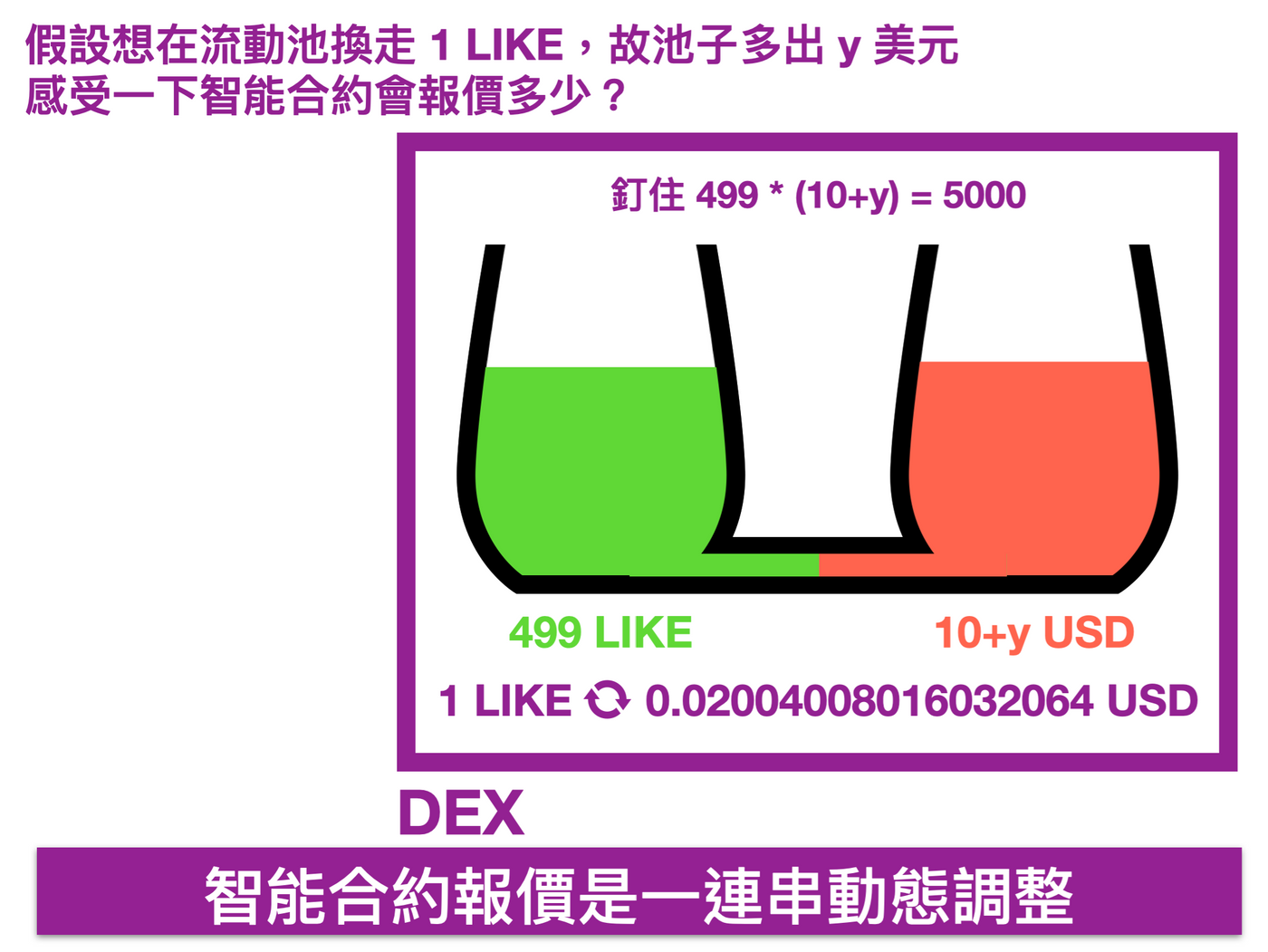
Now you want to exchange 1 LIKE in the liquidity pool, so the amount of USD will increase by y, the question is how much will it increase? This is what the smart contract (mathematical model) has to match. In this example, to solve the equation:
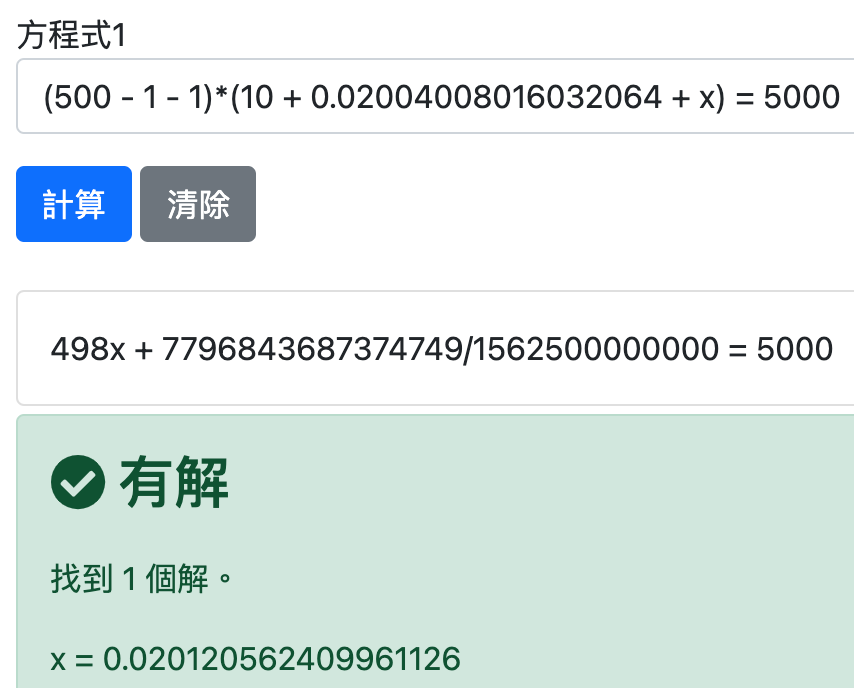
(500 - 1) * (10 + y) = 5000
Find y = 0.02004008016032064, which is also the quote you see on the vending machine. The quote is no longer 1 LIKE = 0.02, it moved.
If you change another 1 LIKE, this time change the name of the variable, increase the USD quantity by x, and get a new quotation of x = 0.020120562409961126 ⇩, it has moved again and is more expensive, and the quotation is a series of dynamic adjustments .
The above statement is represented by a schematic diagram ⇩:
If the two currencies are stable, then the strength of the currency exchange (swap) will increase and decrease. You come and go, like a tug of war. The " quantity ratio " of the two coins is mostly around 500:10 of the original investment. Regardless of the reward, when you want to unbind and withdraw (based on your stake), you can expect to get back the relative amount of the two coins, and The original ratio was similar, for example, it came to 550:11 and the like.
Then you must ask, what if it is unstable? That is, the phenomenon of exchange rate fluctuations on the CEX side.
■ A coin rises relatively sharply (the other coin falls relatively sharply)
Assuming that on the CEX side, LIKE has risen sharply, and the market price has reached 1 LIKE = 0.03 USD, then the keen trader, seeing a batch of very cheap beef 1 LIKE = 0.02 USD on the DEX side, is bound to come here desperately to "move bricks" "Exchange the LIKE (which will increase the amount of USD in the pool), move it to CEX and sell it.
In the previous example, we know that the smart contract quotation is a series of dynamic adjustments , and the “moving bricks” in the same direction also increases the price, until it is similar to the CEX side and is unprofitable. The schematic diagram is as follows⇩:

■ Impermanent loss
Finally we can talk about the concept of Impermanent Loss.
The word "impermanence" is a bit abstract, but it is actually more aptly translated as non-permanent loss or non-permanent loss , meaning that the loss is temporary, on the books, and not realized.
To put it more vernacularly, it calculates the difference between the value of "simply holding two currencies vs. taking liquidity mining" at a certain point in time , returning to the situation of the previous surge (1 LIKE = 0.03 USD), The non-constant loss at this time is calculated as follows⇩:
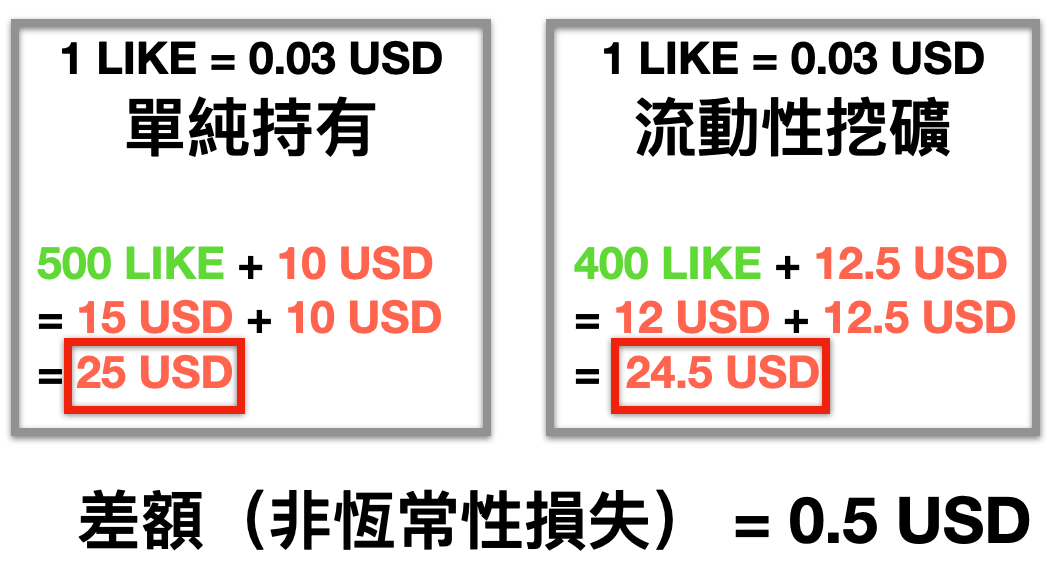
The value itself is not very important, it is good to feel "there is a difference".
So simply holding coins will make more money? Not necessarily, because the coin pool reward is not considered in the explanation, just to let everyone know that when participating in liquidity mining, the more unstable the currency, the greater the non-constant loss on the account.
I think the concept of non-constant loss is like a mapping of opportunity cost in economics. The former emphasizes the risks of doing something, and it is not necessarily a loss if you do nothing; the latter focuses on the cost of not doing something (giving up opportunities), and it is not safe to maintain the status quo .
⚠️ Highlights:
① The "price determination" of CEX and DEX has different systems.
② AMM smart contract quotation is a series of dynamic adjustments.
③ How do bricklayers realize arbitrage.
④ Non-constant loss is to calculate the difference between the value of “simple currency holding vs liquidity mining” at a specific point in time.
⑤ When participating in liquidity mining, the more unstable the currency, the greater the non-constant loss on the book.
Thank you for seeing this, and attach my link to [ Appreciate Citizens 2.0 ] [ Iron ] [ Other Platforms ], welcome to visit ❤️.
🌱 Season 3 community activities in progress compilation form + description
❏
🌱 Become my appreciative citizen👇
https://liker.land/leo7283/civic was invited to enter the fireplace
❏
🌱 Tracking [ Zhongshu Nervous System ] broadcast information is not missed
Good Books Quotes/Book Market News/Mind Map
❏
🌱 I am on other platforms👇
【 Facbook | Mastodon | Medium | Vocus | Potato 】
Like my work?
Don't forget to support or like, so I know you are with me..
Comment…