Unlocking the Power of Battery Energy Storage Systems: A Revolution in Energy Management
Introduction
In today's world, the demand for clean and sustainable energy solutions is greater than ever. One technology that has emerged as a game-changer in the realm of energy storage is the Battery Energy Storage System (BESS). With its ability to store excess energy and provide it when needed, BESS is revolutionizing the way we manage and utilize electricity. In this article, we will delve into the workings of a battery energy storage system, explore its benefits and applications, and examine its potential to transform the energy landscape.
Understanding Battery Energy Storage Systems
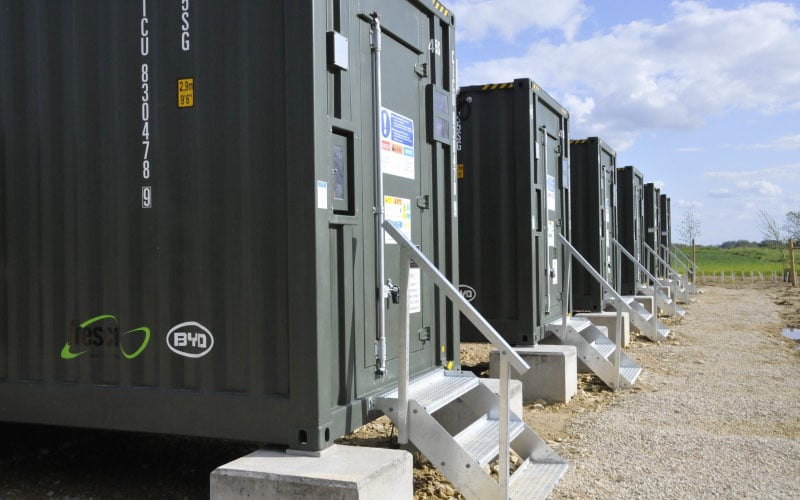
A Battery Energy Storage System consists of rechargeable batteries, power conversion systems, and control electronics. It acts as a reservoir for excess electricity, which can be drawn upon during times of high demand or when renewable energy sources are unavailable. The batteries within a BESS can be charged using various sources such as solar, wind, or grid power, making it a versatile solution for storing energy from both renewable and conventional sources.
Benefits of Battery Energy Storage Systems
Grid Stability and Energy Management: One of the significant advantages of BESS is its ability to enhance grid stability by balancing the supply and demand of electricity. It can absorb excess energy during times of low demand and inject stored energy back into the grid during peak hours. This capability helps to stabilize the grid, reduce power fluctuations, and prevent blackouts.
Integration of Renewable Energy: BESS plays a crucial role in overcoming the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. It enables the efficient storage and utilization of excess renewable energy, which can be dispatched when needed, thus ensuring a consistent and reliable power supply.
Load Shifting and Peak Demand Reduction: Battery energy storage allows for load shifting by storing electricity during off-peak hours when demand is low and releasing it during peak hours when demand is high. This practice helps to alleviate strain on the grid during periods of high energy consumption, reducing the need for additional power generation capacity and mitigating the reliance on fossil fuels.
Ancillary Services and Backup Power: BESS can provide ancillary services to the grid, including frequency regulation, voltage support, and reactive power control. Moreover, in the event of a power outage or emergencies, battery storage systems can serve as a backup power source, ensuring uninterrupted supply to critical facilities such as hospitals, data centers, and residential homes.
Applications of Battery Energy Storage Systems
Renewable Integration at Scale: As renewable energy penetration continues to increase, battery energy storage systems play a vital role in integrating large-scale renewable projects into the grid. They help to smooth out fluctuations, maximize energy utilization, and ensure a steady power supply.
Microgrids and Remote Areas: In remote areas or places with unreliable grid infrastructure, BESS can be deployed to create microgrids, combining renewable energy sources with energy storage. This approach improves energy access, enhances resilience, and reduces dependence on fossil fuels.
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure: The rising popularity of electric vehicles (EVs) necessitates the development of robust charging infrastructure. Battery energy storage can support fast-charging stations, provide load management, and optimize the utilization of renewable energy for EV charging, making it a critical component of the electric mobility ecosystem.
Industrial and Commercial Applications: Industries and commercial establishments can leverage battery energy storage to optimize their energy consumption, reduce peak demand charges, and enhance energy efficiency. Large-scale battery systems can help businesses manage their electricity costs effectively and contribute to a greener future.
Conclusion
Battery Energy Storage Systems are transforming the energy landscape by enabling the efficient storage and utilization of electricity from renewable and conventional sources. They offer numerous benefits, ranging from grid stability and renewable energy integration to load shifting and backup power. As the technology continues