新手指南,R 語言基本教學
學習過程中的一點心得整理。
前言
先自首這絕對是一個不專業的 R 語言分享,身為一個 Computer Science 人時不時就有幫人解決疑難雜症,無論是討論演算法、程式或是有人跨系修課也會拿著熱騰騰的作業來問你,秉持著一顆熱愛學習的心,筆者就這樣幫助同學邊討論邊寫了 R 的作業。
因此,決定把學習到的東西稍微記錄下來。畢竟,教學文永遠是越多越好,通常遇到程式問題時,筆者總是耐著性子一篇一篇教學文看,你永遠不知道會不會下個轉角,就遇到跟你一模一樣需求,甚至連 Code 都幫你寫好的大神。
有鑒於筆者讀的文獻英文居多,所以文章中的專有名詞就以英文呈現。
快速瀏覽
節省閱讀時間,下面羅列文章有用到的 Function。
- length() - grepl() - read.table() - rowMeans() - colMeans() - dim() - row.names() - names() - hist() - log() - ifelse() - cbind() - factor() - table() - subset() - rnorm()
建立環境
筆者很懶,最討厭處理設定和安裝環境,以我多年當助教、或是當 Mentor 的經驗,對入門者而言最難的永遠不是程式,而是令人摸不透的環境設置,因此這邊介紹大家一個好東西,叫做 Google Colab。
Google 出的這款雲端開發環境,使用起來和 Jupyter Notebook 類似,也有支援 R 語言的撰寫,也就是說今天不需要安裝一堆東西,只有輕鬆點開下面連結,開一個 Base-on R 的 Notebook 即可。
The link to new a R Colab notebook 點開就能跑
Google Colaboratory
Edit descriptioncolab.research.google.com
The description of R Google Colab
Google Colaboratory
Edit descriptioncolab.research.google.com
熱身
我們先從裝有字串的 Vector 開始,印出它的長度來看看。
library(ggplot2) #set the library
nouns <- c("apple", "banana", "cat", "dog", "egg", "fox", "good")
length_of_nouns <- length(nouns)print(nouns)

接著來試試看使用 Indexing 建立新的 index
#using indexing to create a new index test_1 <- nouns[c(1:4)] test_3 <- nouns[c(1,3:4,7)] #Get 1,3,4 and 7 vaules print(test_1)print(test_3)

接下來反轉一下 Vector。
# reverse oreder indexing test_4 <- nouns[c(7:1)]print(test_4)

資料處理
接下來進入讀檔案處理的環節!
首先介紹資料處理第一關,在 Google Colab 讀資料,只能說非常難筆者卡了半個小時,在 Python 中要用程式與 google drive 做連結。經過好一陣子的折磨,發現超簡單時差點把自己掐死,最左邊有個很像資料夾的東西,點開就可以把檔案傳上去了。
介紹資料集
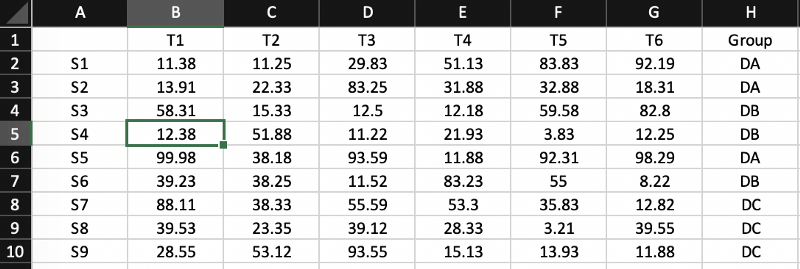
# Read file as dataframe
data <- read.table('test.txt', header = TRUE)
# Columns
namenames(data)
# Rows name
row.names(data)
# Dimension of the data
dim(data)

計算 Columns &Rows 的 Mean
# Cal row's meanrow Means(data["S2",1:6]) # Cal col's mean with different function colMeans(Filter(is.numeric, data)['T2'])

以 Column 的 Value 作為 Key 找出對應的 Rows
# Single groupby
GroupBy <- data[grepl("DB", data[["Group"]]) , ]
# Multiple groupby
MultiGroupBy <- data[grepl("DA", data[["Group"]]) |
grepl("DC", data[["Group"]]) , ]

極簡單常態分佈篇
首先來進行一下假設,一個班級有500個學生,全校平均為 70 分,標準差是 10 分,填入公式後會得到下面的程式。
# Normal Distribution x <- rnorm(200, mean=68, sd=10) # Curve the score by adding 11% cur_x <- 1.11*x # Min min(cur_x) # Max max(cur_x) # Standard Deviation sd(cur_x) # Mean mean(cur_x) # Plot as histogram hist(cur_x, probability=TRUE)
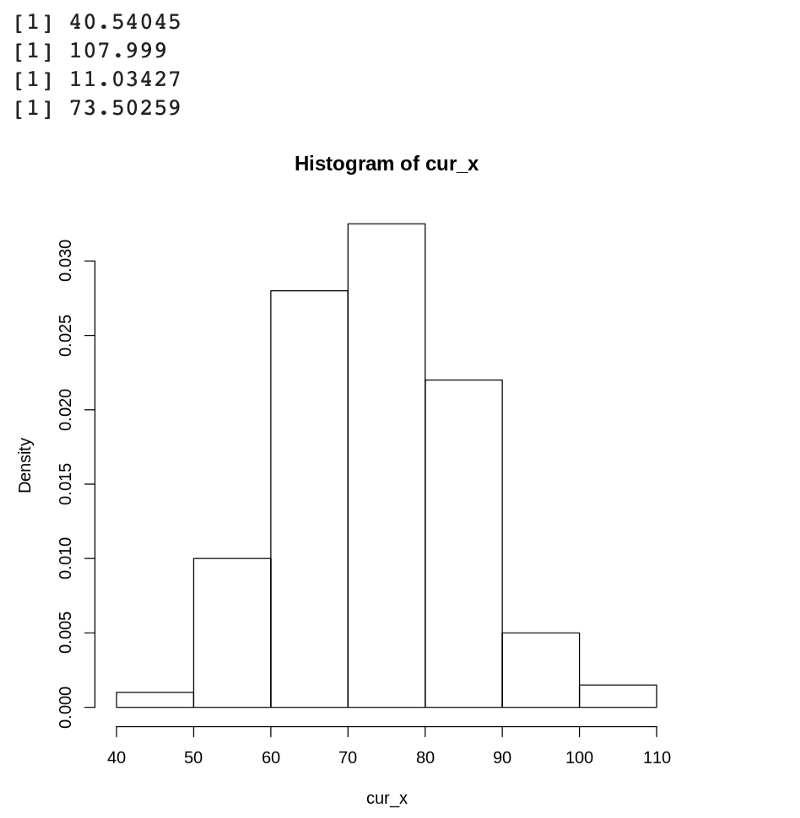
資料處理 Part 2
資料介紹
現在來另一個魚骨頭長度資料集。
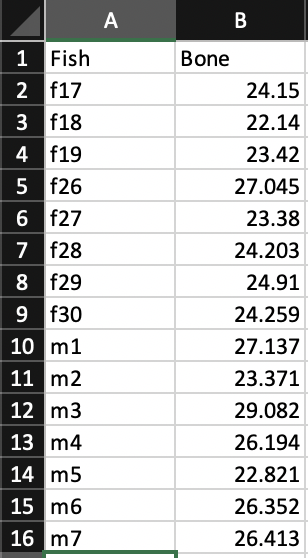
If/else 使用 & Column 與 dataframe merge
# 先取出 data 中 Fish 的 vector
test <- data[["Fish"]]
# 用它來判斷如果裡面有 f 則設為 female, 否則為 malese
x <- ifelse(grepl("f", test), "female", "male")
# 將其 Merge 回原資料並把 Column 設為 Sex
x <- cbind(data, Sex = sex)
Natural Log 使用以及 Table()
# 以 Sex 欄位建立一個 Table 統計裡面 Values 出現次數 occurences<- table(x["Sex"]) # 將 Bone 欄位進行 Natural Log after_log <- log(x[["Bone"]])hist(after_log, probability=TRUE)
使用 Logical Indexing 和 Subset 處理資料
解釋一下 Logical Indexing,簡單來說就是建立一個與目標欄位等長且只有 True 或 False 的 Vector,並在其中進行挑選,把要留下的資料對應的位置設為 True,其餘的設為 False 。接下來在做 Logical Indexing 時,就會自動留下為 True 的資料。
# init datadata <- read.table('fish.txt', header = TRUE)
# 以 vector 的方式取出 Fish
test <- data[["Fish"]]
# 以 if/else 的方式判斷,與骨頭長度有沒有超過 25cm
# 用 data$Bone 類似變數的概念,可看作為 data["Bone"]
over <- c(ifelse(data$Bone > 25.0, TRUE, FALSE))print(over)
# 將產生出的 over(vector) 做 logical indexing 產生T
t <- test[over]print(t)
# 以 Sebset() 的方式處理資料。
sub <- subset(data, Bone < 25.0)print(sub)

後記
不專業教學文在這邊告一段落,只要能夠照著上面的步驟嘗試,相信你也能掌握一些資料處理的技巧,下方筆者羅列了許多厲害大神的教學文,想再更精進的大家,不要錯過了。
關於作者
關於作者: Shane 喜歡寫文章的理科男孩。 目前人在紐約攻讀 Master of Computer Science 不定期分享一些留學、工作、生活、旅遊的有趣故事們。 ↓如果喜歡我的文章,或覺得有趣請幫我分享或拍20下手↓↓↓↓或是買杯咖啡給我,支持我持續文字創作。
Hsien Yi Liu on Buy Me A Coffee
Buy Hsien Yi Liu a coffee. Join other supporters and enjoy exclusive content, leave a positive note and more.www.buymeacoffee.com
Reference
R 教學 - G. T. Wang
這裡提供 R 語言的入門教學、進階使用技巧與範例等相關文件。 R 語言入門教學 這是一系列適合初學者快速入門的 ...blog.gtwang.org
輕鬆學習 R 語言:起步走
關於 R 的特性、開發環境與開始寫 Rmedium.com
R - Functions
A function is a set of statements organized together to perform a specific task. R has a large number of in-built…www.tutorialspoint.com
Learn R | Codecademy
R is a popular language used by data scientists and researchers. If you are working with data, R is a fantastic…www.codecademy.com

