【法規工具文】Quick-guide on Software Pre-Cert Program(4) — Streamlined Review
【導讀】本文最初用英文寫作,目的是保留FDA原意。而本版的目的為工具用文章,故用中文註釋以便快速抓到重點,但細節部分還是建議細讀英文說明
FDA避免重複的審核浪費兩造的時間,所以提出精簡審核的構想,但前提是廠商須符合CQOE組織卓越性的評鑑。
精簡審核的作法在於(1)消除重複性的資訊(2)用互動的方式提升效能(3)如果可以,則自動化.其最後打算達到的觀念可參考Fig. 1
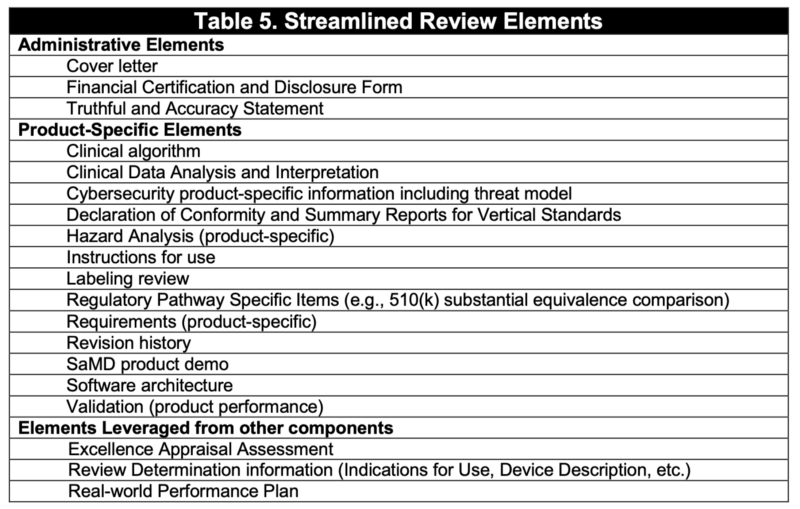
精簡審核的必要文件可參考Table 1.
The principal objectives of establishing the streamlined premarket review process component of the Software Pre-Cert Program are to identify the elements necessary for a premarket review and to develop a premarket review process that provides reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness of a software product from a precertified organization.

Elements necessary for assuring safety and effectiveness in premarket review
FDA proposes that certain elements traditionally reviewed in a premarket submission for a SaMD product can be evaluated at the organization level during the Excellence Appraisal and at the product level during Review Determination.
【導讀】精簡審核的必要文件
Table 1 includes the elements that would be reviewed during a Streamlined Review in order to provide a reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness at the point of market entry.
Interactive Streamlined Review Process for Premarket Review
There are common review elements among 510(k) submissions, De Novo Requests, and PMA applications. When using a reduced set of elements described in Table 1, the Streamlined Review process is focused on what the subject device is and on its intended use. While there are unique elements of Streamlined Review for each of these processes, FDA finds that the processes converge conceptually.
Thus, FDA presents a generic regulatory pathway in Figure 1 that depicts the generic process FDA would propose to follow in the Pre-Cert program, regardless of the regulatory pathway.
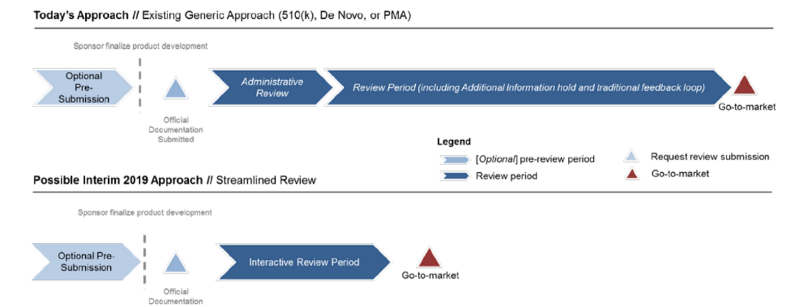
【導讀】FDA精簡審核流程如下,(1)消除重複性的資訊(2)用互動的方式提升效能(3)如果可以,則自動化
FDA is developing a Streamlined Review process that a) eliminates duplicative information, b) is interactive, and c) where possible, is automated.
A) Eliminate Duplication. Duplicative information is presented in many parts of the traditional documentation. For example, for a SaMD product, the software/firmware description typically included in the software documentation is duplicative of the product description, because the device itself is software.
Many of the elements typically found in a device description for a device are the same information that is part of Review Determination. FDA aims to eliminate repetitive information as one means of reducing burden and making the review process more efficient.
B) Interactive. Promoting the use of an interactive review process may contribute to a more efficient review. In particular, enhanced early interaction may benefit and improve the review process because it would expose potential challenges early in the process, so that both parties can proactively plan interactions that move towards the goal of a complete and transparent premarket clearance.
C) Automation. Where possible, automation would be used to streamline the review process and to perform administrative functions. For example, FDA is considering suggestions to develop templates that help the sponsor to determine if the submission is complete before it is submitted to FDA. This automation should shift the focus of the review process to a technical review of the product rather than an administrative review of the package.
The FDA intends to conduct an interactive review supported by automated analysis, where appropriate, and aspires to provide a decision on the marketing of the precertified organization’s SaMD product within a shorter timeline than traditional premarket review processes.
