
123
Thrombolysis track at a glance: Alteplase is the most significant single product, next-generation innovative thrombolytics are the competitive high ground
The effect of cardiovascular disease risk factors on population health has become more significant in recent years. Cardiovascular illness is increasing in prevalence in China, and the advancement of the area of cardiovascular disease therapy has become a significant source of worry.
Thrombolytic therapy is a promising treatment modality for cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial infarction and acute ischemic stroke, and the development landscape of the thrombolytic drugs market continues to evolve in response to industry concerns. Today, the demand for thrombolytic drugs is growing, and the number of players in the industry is increasing, but it is the next generation of innovative thrombolytic drugs that patients and the industry are eagerly awaiting.
Cardiovascular disease is the collective term for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and refers broadly to ischaemic or haemorrhagic diseases of the heart, brain and body tissues caused by hyperlipidaemia, blood viscosity, atherosclerosis and hypertension.
China's cardiovascular disease market to approach $250 billion in the next three years.
According to the analysis of the China Cardiovascular Health and Disease Report 2020, the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in China is on a continuous rise due to factors such as an ageing population, unhealthy diet and lack of exercise. As of today, there are approximately 330 million patients with cardiovascular disease in China. The mortality rate of cardiovascular disease in China is the highest, with a large population base of cardiovascular patients and a high mortality rate. There is a trend of low age, rapid growth among low-income groups and individual clustering, making it one of the major healthcare issues in China.
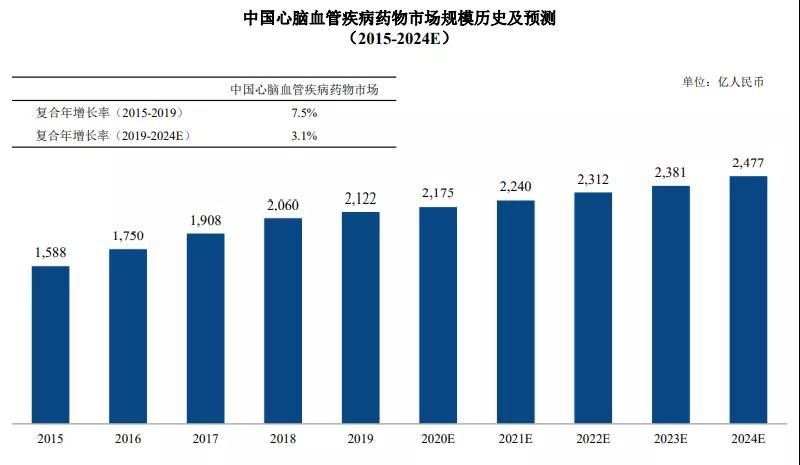
Publicly available information shows that the market size of the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease treatment segment was approximately RMB 212.2 billion in 2019, accounting for approximately 12.99% of the overall size of China's pharmaceutical market. The market size of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases grew from RMB158.8 billion in 2015 to RMB212.2 billion in 2019, with a compound annual growth rate of 7.51%. The market size of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in China is expected to grow to RMB247.7 billion by 2024.
Among these, acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) is a leading cause of death in China's cardiovascular system. It refers to a category of acute myocardial infarction with typical ischaemic chest pain lasting more than 20 minutes and an ECG with typical acute ST-segment elevation.
Treatment of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: PCI procedure and thrombolysis
Usually, acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction is caused by acute occlusive thrombosis induced by coronary plaque damage, which leads to massive myocardial necrosis due to prolonged blood supply obstruction, thereby endangering the patient's life.
If patients can receive effective reperfusion therapy early, especially within 3 hours of coronary occlusion, it can save large areas of dead myocardium, reduce the size of the infarct and protect the ventricles.
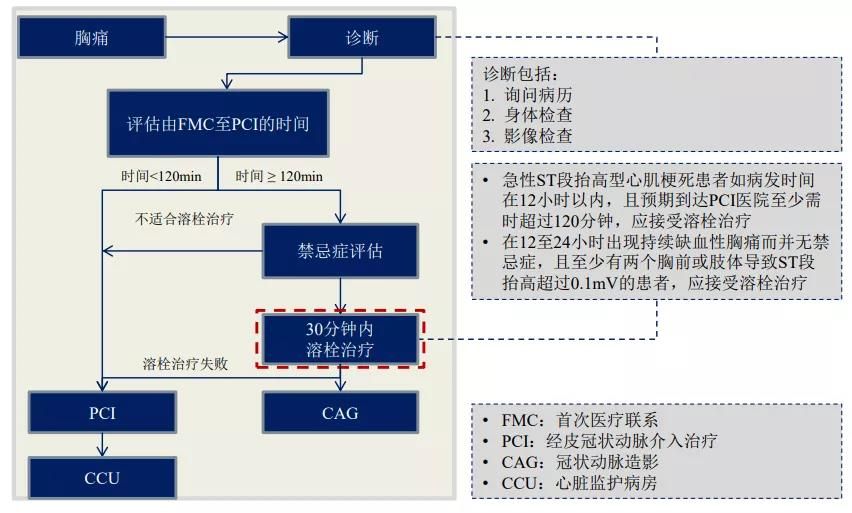
According to the Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Acute ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction and the Guidelines for the Rapid Treatment of Acute Coronary Syndromes, acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction is currently treated by both PCI and thrombolysis.
However, PCI is currently only available in hospitals in the more developed cities of China, while small and medium-sized cities and rural areas cannot perform PCI due to a lack of medical resources.
Thrombolysis is the treatment of choice for patients in developed cities who are unable to undergo PCI, for example, when an acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction occurs within 12 hours and the expected arrival time at the PCI hospital is more than 120 minutes; and, when the time between the initial medical contact and the time when PCI is available is more than 120 minutes.
Acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction is treated in the following ways.
Thrombolysis has specific advantages over PCI, namely that it is relatively inexpensive and less traumatic for the patient and that it is more accessible in our current medical situation.
Overview of common thrombolytic drugs: Alteplase as the most extensive single product, Puyuk to deliver prospects
At present, the most significant single product of thrombolytic drugs in China is alteplase (rt-PA), accounting for about 70.23% of the market size of thrombolytic drugs in China, with sales scale of about RMB 1.407 billion. The second-largest thrombolytic drug is urokinase, accounting for 14.67% of the market size of thrombolytic drugs in China, with a sales volume of about 294 million yuan. The core product of the leading domestic thrombolytic company, Tianshi Li, is the third-largest thrombolytic drug product in China, accounting for 12.24% of the market size of thrombolytic drugs in China.
It is understood that Puyuk only has an approved indication for acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, which is a relatively small market share compared to alteplase and urokinase due to its single indication range. However, with the approval of new indications for Puyuk, its market share may be further expanded in the future.
Puyuk is a fibrin-specific fibrinogen activator that is injected intravenously into the circulatory system in a relatively inactive state. It has minimal impact on endogenous fibrinogen in plasma, which is mainly activated on the thrombus surface by kinin-releasing enzyme or fibrinase, partly converting it into a double-chain urokinase that activates fibrinogen attached to the thrombus surface in a changed conformation. The latter induces fibrinolysis in the fibrinogen adhering to the changed thrombus surface, resulting in the partial disintegration of the thrombus fibrin.
When the E fragment of thrombofibrin is exposed, Puyuk directly activates the fibrinogen bound to the two amino acid residues at the C-terminus of the fragment, forming a ternary complex "Puyuk + fibrin + fibrinogen", which increases the activity of Puyuk by 500 times and produces a large amount of fibrinolytic enzymes, resulting in the rapid degradation of thrombofibrin and the dissolution of the thrombus.
Unlike alteplase, the most commonly used thrombolytic drug in China, Puyuk does not form covalent complexes with protease inhibitors in the plasma. Therefore, the concentration of Puyuk and protease inhibitors in the blood is not reduced. The presence of this inhibitor is directly related to the prevention of systemic haemorrhage, and higher inhibitor concentrations are beneficial in reducing the rate of intracranial haemorrhage in patients.
Bacterial vector YB1 combines with urokinase to expand the new thrombolytic drug pipeline.
It is worth noting that traditional thrombolytic drug therapy also has a pain point, that is, the commonly used thrombolytic drugs on the market, such as recombinant urokinase and rt-PA, have a short half-life of 4-8 minutes, which does not alleviate the onset of acute thrombosis. There is an urgent need for more new drugs or new therapies to effectively alleviate and treat acute thrombosis to meet the market demand.
HKNK YB1 is also currently developing new thrombolytic drugs. Our core technology product, the biomolecular drug delivery vehicle YB1, can carry the thrombolytic enzyme rt-PA to hoard at the thrombus site and can be released at a fixed point, solving the problem of its short half-life, which is a very innovative and cutting-edge attempt in the field of antithrombotic therapy.
Our bacterial vector YB1 is applicable in two main technological fields: YB1 with tumor hypoxia-specific targeting technology can be used as a vector for the efficient delivery of a wide variety of therapeutic agents, including antibodies, messenger RNAs, and proteins, targeting and releasing them in a targeted manner, thereby achieving a tumorolytic effect and developing the world's first tumorolytic bacterial cancer immunotherapy solution.
The combination of YB1 with Urokinase and other thrombolytic drugs for the treatment of various thrombotic diseases is another crucial technological expansion direction for YB1 in addition to tumour immunotherapy. The main feature is that it is carried by YB1 and releases urokinase (Urokinase) at the thrombus site, allowing for rapid, targeted release of thrombolytic drugs.
Of course, it is well known that antithrombotic treatment is not an easy task, and the process of resuscitating patients after the onset of the disease is a race against time. Therefore, the invention and application of effective and innovative therapies and drugs are of particular importance to the healthcare industry. We hope that this innovative product will soon advance into clinical studies and make further progress so that patients can benefit from it as soon as possible.
HKND YB1 is a high-tech biotechnology company focusing on developing innovative drugs in the field of targeted tumour therapy. It holds the world's only patent on oxygen-regulated lysozyme bacteria, and its core technology product, lysozyme bacteria (YB1), has strong efficacy, compatibility, scalability and safety, with a technical principle paper published in a sub-publication of Nature in 2021. At present, the company has laid out 11 product pipelines and is pushing forward the development and implementation in an orderly manner.
喜欢我的文章吗?
别忘了给点支持与赞赏,让我知道创作的路上有你陪伴。
发布评论…