CoinEx Research Institute|Liquid staking: Release the capital value and efficiency of public chain nodes
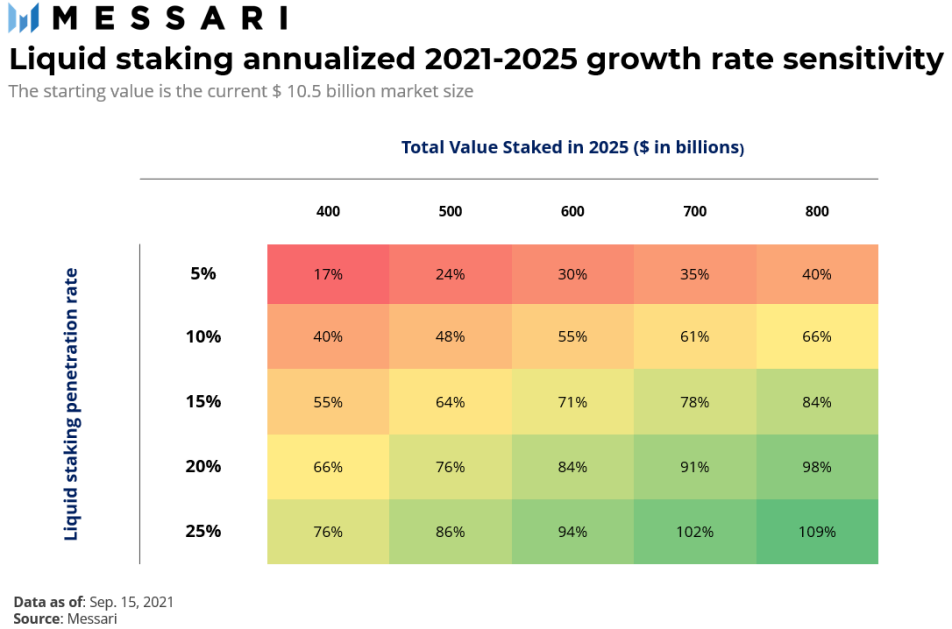
According to incomplete statistics, the current market value of Proof-of-Stake is 312.9 billion US dollars, the global pledge value is 217.94 billion US dollars, and the liquid staking market value accounts for 17.23 billion US dollars, an increase of 70% compared with last October (10.5 billion US dollars). The penetration rate ( The penetration rate refers to the pledged tokens in the liquidity Staking protocol divided by the total value of the market pledge) increased from 7% to 7.9%, and the market potential is huge. According to the estimated growth of the Messari model, it is assumed that by 2025, the annual staking reward will reach 40 billion US dollars, and the average staking rate of return will be between 5% and 10%, which means that the total market value of pledged tokens will be between 400 billion US dollars and 800 billion US dollars. between US dollars.
The decentralized and liquid pledge market will be an unexplored potential market linking major public chains, Ethereum 2.0, DeFi and many other markets. It will further tap and release the value of capital liquidity and improve efficiency. Below we will go back to the history of POS, analyze the current market situation, and discuss the decentralized liquidity staking solutions emerging in major public chains.
History of Traditional Staking
As one of the current cryptocurrency trends, staking has a long history. With the birth of EOS and other star-level POS networks, the blockchain network verifier does not need to purchase a large number of mining machines to perform heavy hash operations like the POW consensus mechanism, but only needs to pledge a certain amount of generation to the blockchain network. Coin deposit and running the project code can become a node or a verification node, and can participate in the process of recording the ledger of the blockchain network, or participate in the block generation to earn block rewards and handling fees. At the same time, the market has begun to develop pledge services for ordinary users who do not have technical capabilities to participate in nodes. Users can choose a centralized exchange or a decentralized wallet to select their favorite nodes to pledge, and share nodes with node verifiers. The block and fee rewards are divided, while the nodes attract users to pledge to obtain rewards through the stability of their nodes, management fee competition and other services, improve their node rankings, and obtain the license rights and block rewards of validating nodes.

To summarize, in staking, users lock or keep their funds in a crypto wallet to participate in maintaining a PoS-based blockchain system. Both Proof-of-Stake and Proof-of-Work share the same goal of achieving consensus while rewarding participation. However, in the course of the game, unfair competition or conspiracy such as vote bribery and vote collusion often occur between PoS network nodes and verification nodes. One person operates multiple verification nodes maliciously, jeopardizing the security of the blockchain PoS network.
For users, participating in the pledge service of centralized exchanges is far less rewarding than decentralized pledge income. PoS tokens purchased in centralized exchanges are often borrowed and lent to the nodes of the exchange’s PoS network. With a large amount of Token assets from users, a centralized exchange can become a verification node to earn block rewards and handling fees, while other third-party verification nodes can only rely on their own purchase of a large number of Tokens for pledge, and the competition pressure is too great.
During the market downturn of 2018-2019, traditional staking has a coin-standard rate of return ranging from 3.12% to 131.24%, which is far less than the loss caused by the decline of the fiat-standard market. The essence of the income is the annual inflation of the PoS network.
The rise of new staking markets
But since 2020, the prevalence of DeFi, the rise of major public chains and their ecological projects, and the development of the Ethereum Beacon Chain have all given token holders more ways to earn and stake tokens. According to the statistics of Stakingwards, as of March 15, the global pledge has reached 199.891 billion US dollars, and the global pledger has reached more than 4.54 million, with an annualized income of 21.423 billion US dollars. It is a difficult trade-off whether to choose a pledge node to maintain network security or to participate in DeFi-Farming to obtain high returns. Even pledges such as DeFi lending, AMM-liquidity, and mining rewards make investors lose their original asset liquidity, and loss of liquidity means loss of value. In addition, the lock-up period and waiting period make investors short-term. With the loss of control over assets, liquid mortgages came into being.

Liquid pledge
Liquidity Staking refers to the process by which users obtain liquidity by staking their assets. The process starts with investors staking their tokens (i.e. ETH or other mainnet tokens) into a protocol, which does the staking on the investor's behalf, and then mints a 1:1 for the investor's claim asset Liquid staking token Coins, then the staking rewards will be generated by Liquid staking tokens, which is similar to the case of decentralized exchange LP tokens . These Liquid staking tokens can be exchanged or used as collateral to borrow assets, in fact, it unlocks additional revenue streams in addition to staking rewards. Liquid staking tokens are instantly redeemable, allowing investors to get back their original tokens without waiting for an unlock period . When staking tokens to mint Liquid staking tokens, investors can choose validators from the validators provided by the protocol used.
This article will be divided into two chapters to review the projects of major public chain liquidity staking solutions.
1. Ethereum 2.0 pledge
The technical complexity of Ethereum 2.0 is beyond the reach of ordinary users, and the minimum deposit requirement of 32 ETH is becoming increasingly out of reach for ordinary users. To enable the transition to Ethereum 2.0 in a safe and controlled manner, staking has an illiquid lock-up period of 18-24 months.
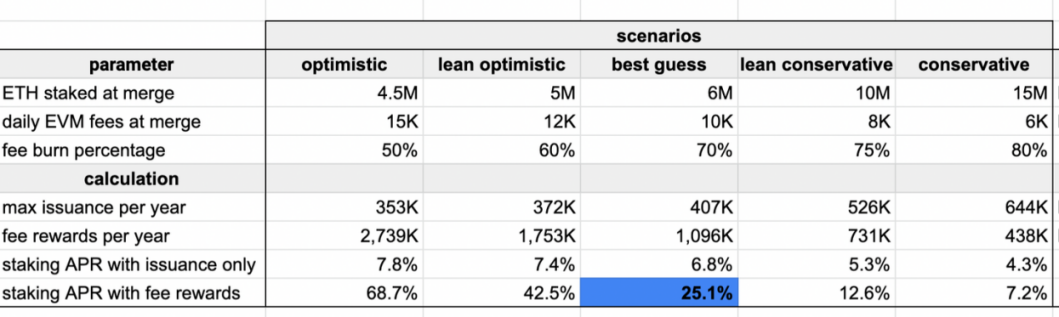
These restrictions can keep less sophisticated users out of the “lucrative” Ethereum 2.0 staking market; the prospects for real yields on ETH 2.0 staking are also compelling. According to a model created by ethereum researcher Justin Drake, the APR of ETH pledged can eventually reach 25% or more.
1) Lido
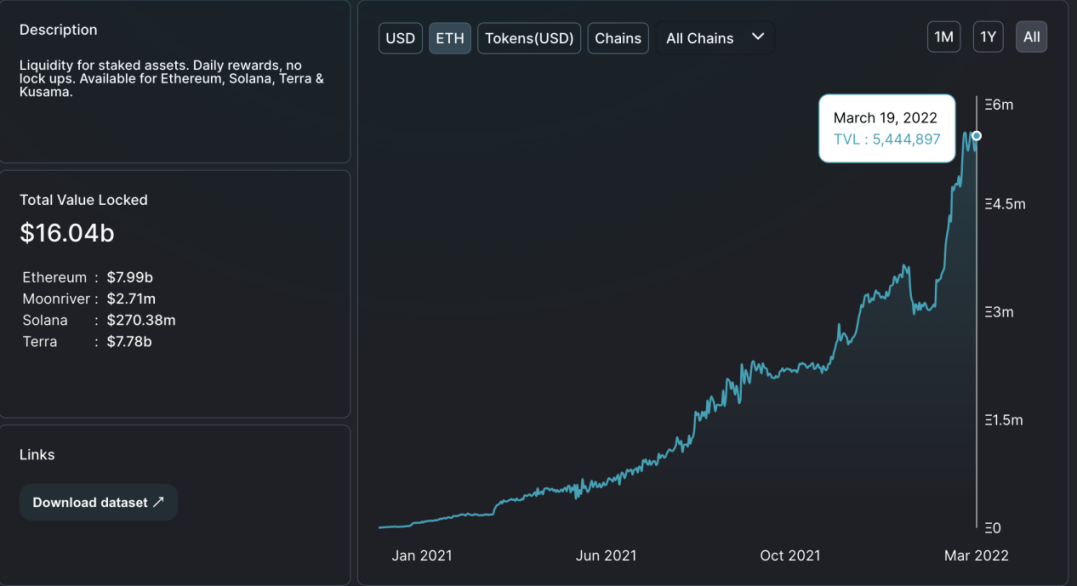
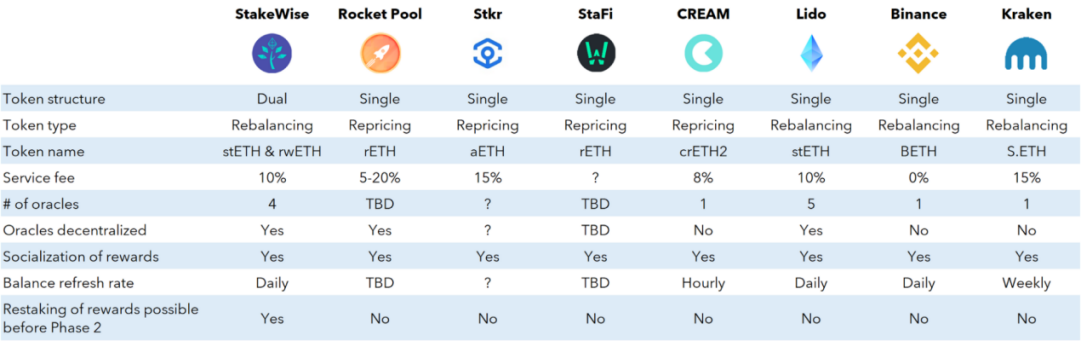
As a leading project of liquid staking solutions, Lido's huge lock-up value and liquidity brought about by its first-mover advantage have already discouraged many similar solutions. According to DefiLlama data, Lido already has more than 33.7K stakers and a TVL of about $16.04 billion. The staked Ethereum is worth about $7.99 billion (about 2.54 million ETH). The staked Terra is worth about $7.48 billion (about 84.68 million LUNA deposits). The staked Solana is worth approximately $266.47 million (approximately 2.89 million SOL deposits). Currently, ETH, Solana, Terra, Polygon, Moonbeam, Anchor and other chains and protocols are supported.
Lido is a decentralized liquid staking solution built on Ethereum 2.0's Beacon chain, managed by the Lido Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO). The goal of Lido is to allow users to stake ETH without losing the ability to trade or use the token. As a decentralized infrastructure for issuing liquidity tokens (stETH), Lido is safer than staking on centralized exchanges, and more flexible than staking by users:
l Allow users to get staking rewards without fully locking ETH;
l Allow users to get rewards without any restrictions by paying a small deposit, not necessarily 32 ETH;
l Reduce the risk of loss of deposit due to software failure or malicious third-party behavior;
l Provide stETH as a building block for other applications and protocols (such as mortgages or other DeFi solutions).
Method to realize
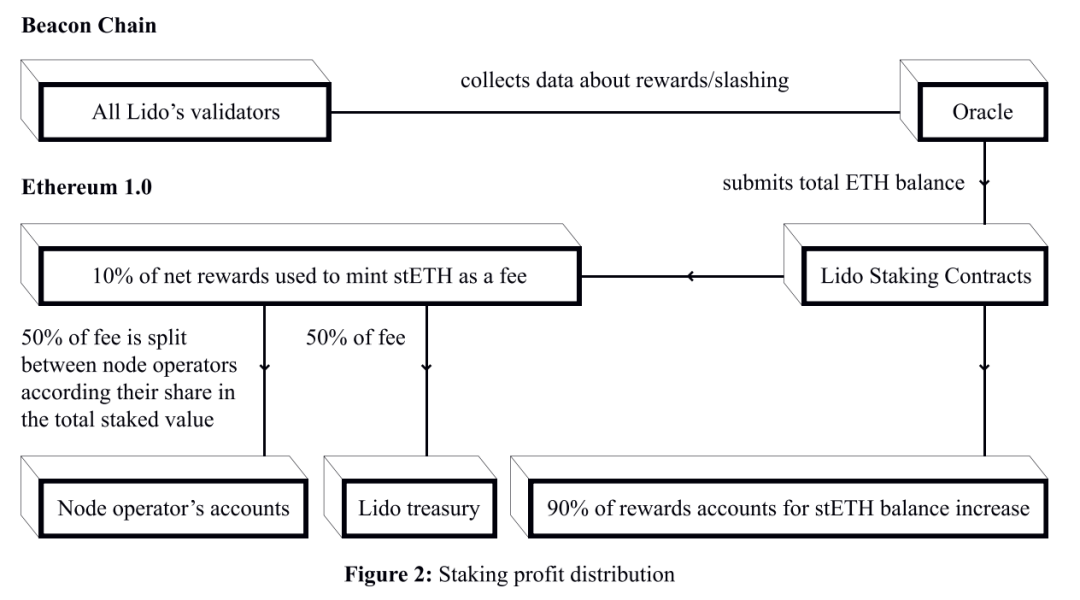
To tie ETH to Lido, users send ETH to a smart contract and receive stETH tokens in return. stETH tokens represent tokenized staking deposits. stETH tokens can be held, traded or sold. The total stETH balance is the sum of deposited ETH and associated rewards minus validator penalties.
All deposits in Lido are divided by 32 ETH and distributed to node operators who use these deposits for verification. Node operators do not have direct access to the user's ETH.
Funds are deposited into the Lido Protocol smart contract and then locked into the Ethereum Proof of Stake deposit contract. The threshold signature account controlled by the Lido DAO is designated as the withdrawal address. Staking Ethereum can only be withdrawn when transactions and smart contracts are implemented on Ethereum 2.0 (expected in Phase 2).
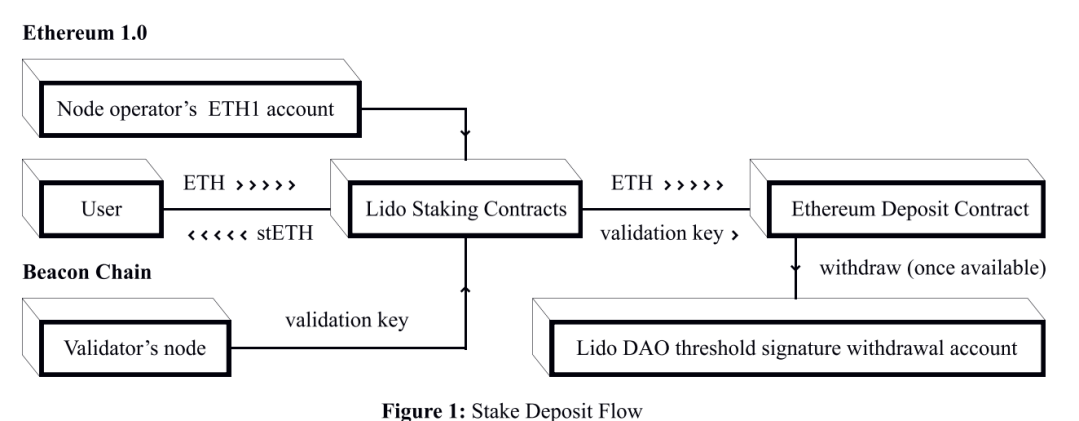
The communication network between the Ethereum 1.0 part of the system and the beacon chain is performed by an oracle designated by Lido DAO. They monitor the node operator's beacon chain and submit the corresponding data to Lido's Ethereum 1.0 smart contract.
Token economy
stETH token
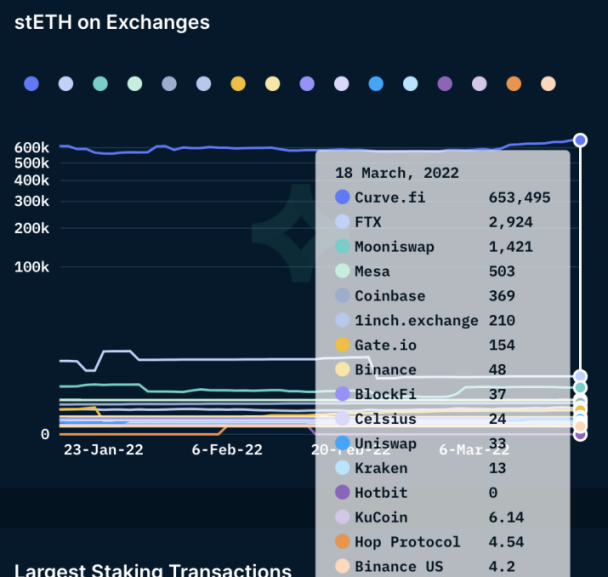
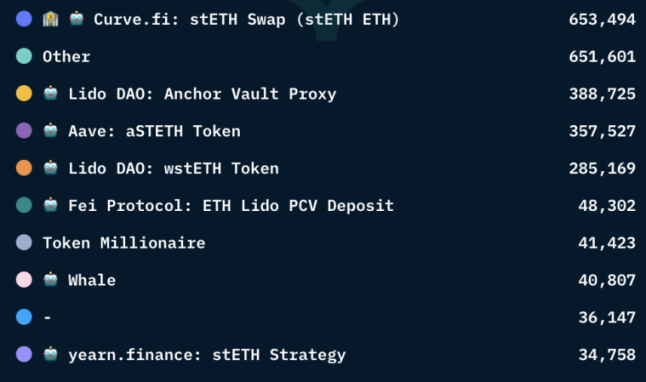
Lido makes the stETH balance track the corresponding ETH balance on the beacon chain. A user's stETH balance corresponds to the amount of ETH a user can receive, and withdrawals are instant. At present, the balance of stETH in centralized and decentralized exchanges is constantly increasing, and the transaction demand is constantly rising. At the same time, it has emerged in major DeFi protocols. The balance in Curve.fi has exceeded 650,000. The Curve protocol is for those who will flow Users who deposit the stETH-ETH pool in the protocol and pledge the obtained LP Token crvSTETH will provide CRV Token rewards; in addition to curve, stETH also occupies a good market in the AAVE lending platform and Yearn and other protocols. The income application scenario is enough to show that the application of stETH in the DeFi field is developing rapidly.
LDO
LDO is the protocol governance token, and the Lido DAO manages a series of Lido protocols including Ethereum. The Lido DAO determines key parameters of the Lido protocol (such as fees) and performs Lido upgrades. Lido DAO members govern the Lido Protocol to ensure its efficiency and stability.
Node strength
As a provider of ETH/ETH2.0 and even multiple public chain liquidity staking solutions, the strength of cooperative nodes is the key to ensuring the security and income of the protocol and user assets, node production and income, network security and not being punished. At present, there are more than 22 verification nodes in cooperation, all of which are well-reputed node operators who have been deeply involved in the industry for many years, providing good support for the normal operation of their protocols and stable income.

risk
With Lido approaching 20% of all validators on the Ethereum network, further capital inflows will begin to threaten the security of the Ethereum network. If the validators of the Lido protocol occupy 50% of the Ethereum network (they may rise in the short term), the returns from stETH will not decline, but the value and security of the Ethereum network itself may be in this case. will suffer irreparable damage. So the only way at this point is to move funds to more other liquidity solutions that are not yet heavily collateralized.
2) Rocketpool
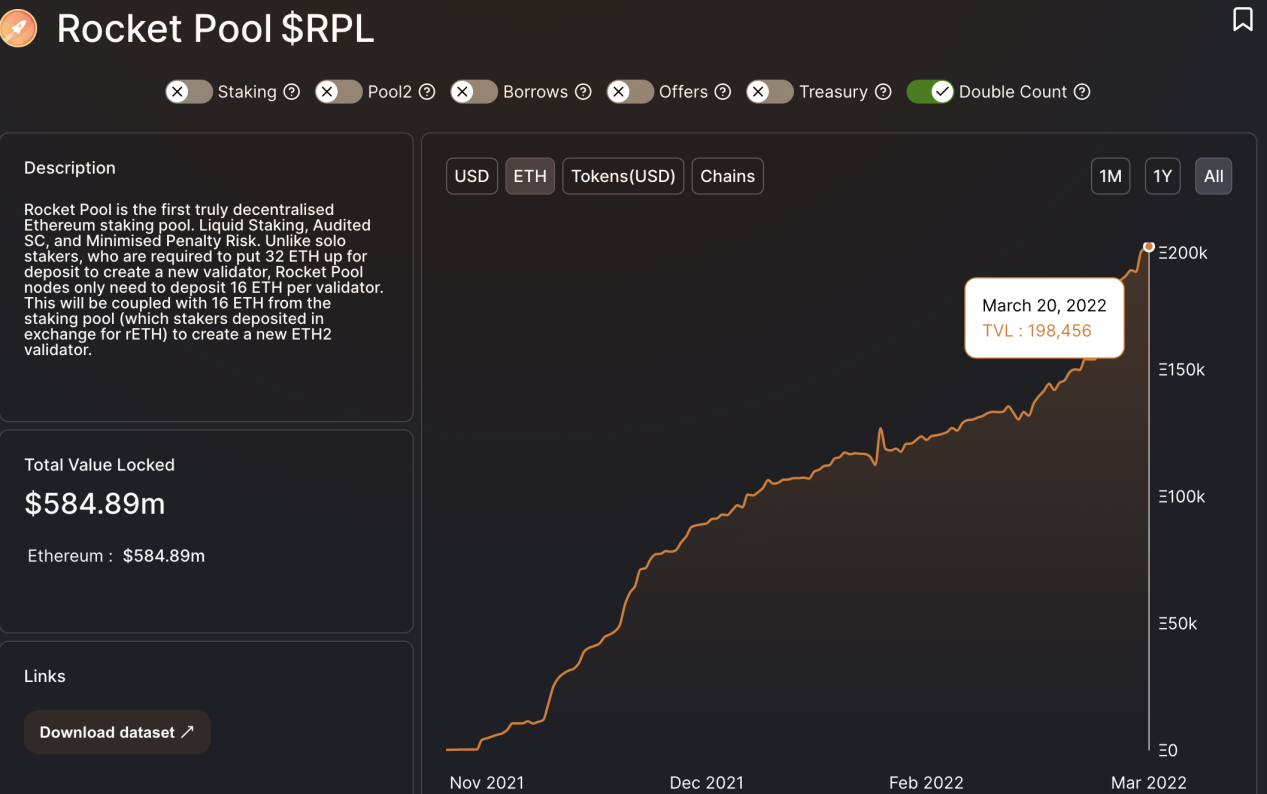
As the first truly decentralized and permissionless Ethereum 2.0 staking base layer protocol, Rocket Pool emphasizes the non-custodial and trustless nature.
According to DefiLlama data and official website, the current TVL of Rocket Pool is about $585 million (about 198,450 ETH).
Agreements and Staking as a Service
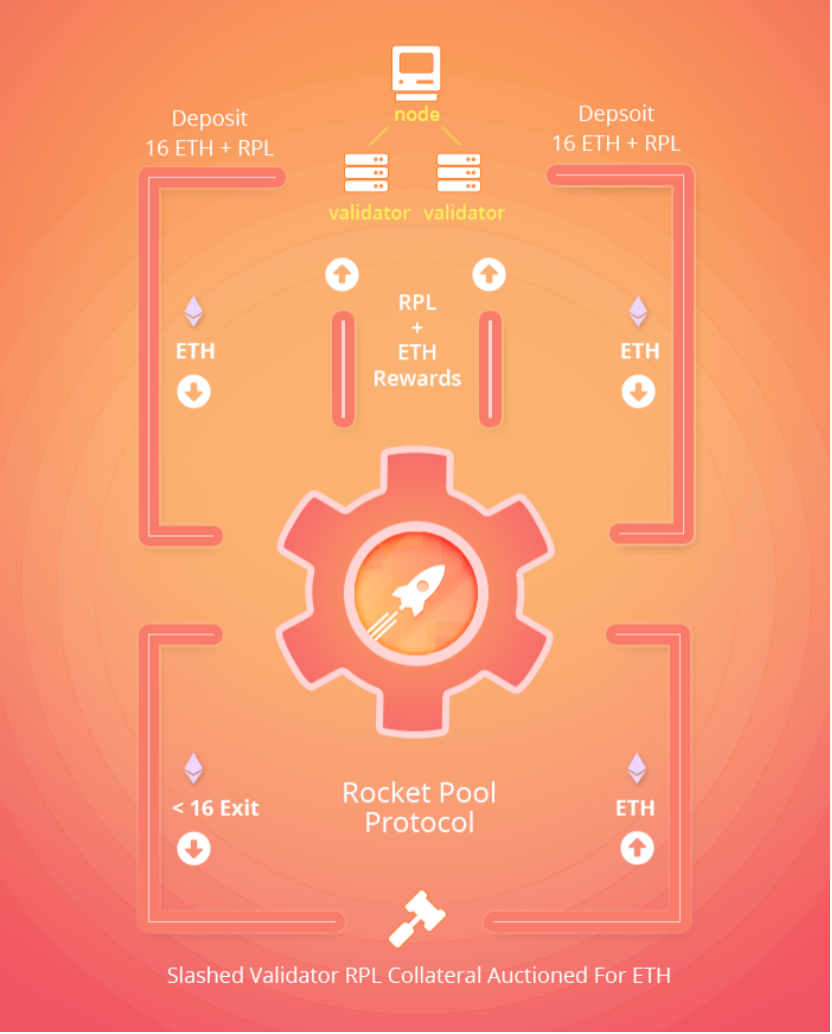
Unlike individual stakers who need to deposit 32 ETH to create a new validator, Rocket Pool nodes only need to deposit 16 ETH for each validator, which will be the same as the 16 ETH from the staking pool (the stakers deposit in exchange for rETH) to create a new ETH2 validator. This new validator is called minipool. As a node operator, you will stake the 16 ETH you deposit and the 16 ETH representing the protocol. Of course, the protocol also allows users to pledge 32ETH. When depositing ETH, nodes must now also deposit a minimum amount of RPL (Rocket Pool Platform Token) as collateral in case they incur any penalties.
Token economy
rETH is not simply 1:1, rETH represents how much ETH the user has deposited and the time when the user has deposited it. The value of rETH is determined by the following ratios:
rETH:ETH ratio = (total amount of ETH pledged in the platform + beacon chain reward)/total amount of ETH pledged in the platform
rETH:ETH ratio = (total ETH staked + Beacon Chain rewards) / (total ETH staked)
This means that the value of rETH always increases effectively relative to ETH. The rETH/ETH exchange rate is updated approximately every 24 hours based on beacon chain rewards earned by Rocket Pool node operators.
Suppose users stake at the beginning of 1 ETH = 1 rETH. Deposit 10 ETH and receive 10 rETH.
After a few years, the balance on the beacon chain grows due to validator rewards. Suppose 128 ETH has been staked to Rocket Pool and the sum of all validator balances on ETH2 is 160 ETH. Then 1 ETH will be worth (128/160) = 0.8 rETH; correspondingly, 1 rETH will be worth (160/128) = 1.25 ETH.
RPL token , in addition to serving as the node pledge deposit for Rocket Pool node operators, will also serve as governance tokens and pledge rewards. Rocket Pool Protocol DAO will be responsible for making decisions on RPL inflation, RPL rewards, RPL auctions (Auctions), RPL pledge amount, nodes Settings for commissions, min/max ETH deposit amount for rETH, etc.
The Rocket Pool protocol has two types of nodes, regular binding nodes and oracle nodes. These node operators form the oracle DAO. The main tasks are two main oracle responsibilities: verifying the Minipool validator balance and the RPL:ETH ratio ensuring that the corresponding RPL reward amount received by the node operator is correct.
Rocket Pool's oracle node operator partners are mainly more decentralized node operators and DAO organizations.

3) Stakewise
StakeWise is also a decentralized Ethereum 2.0 staking service protocol. The amount of ETH deposits and rewards will be reflected in sETH2 (staking ETH) and rETH2 (rewarding ETH) minted to stakers in a ratio of 1:1.
Deposit Queue: Deposited ETH first goes to the mining pool contract , where it is held along with other small deposits until it collects the total 32 ETH required for new validators. Once the mining pool contract collects it, it sends these ETHs to the Validator Registration Contract (VRC), which registers a new validator entity on the beacon chain.
After completing the launch phase in the Beacon Chain, newly created validators start earning rewards for stakers in the StakeWise pool. For every ETH reward earned by the pool, StakeWise will mint an equal amount of rETH2 and issue rewards to sETH2 holders every 24 hours.
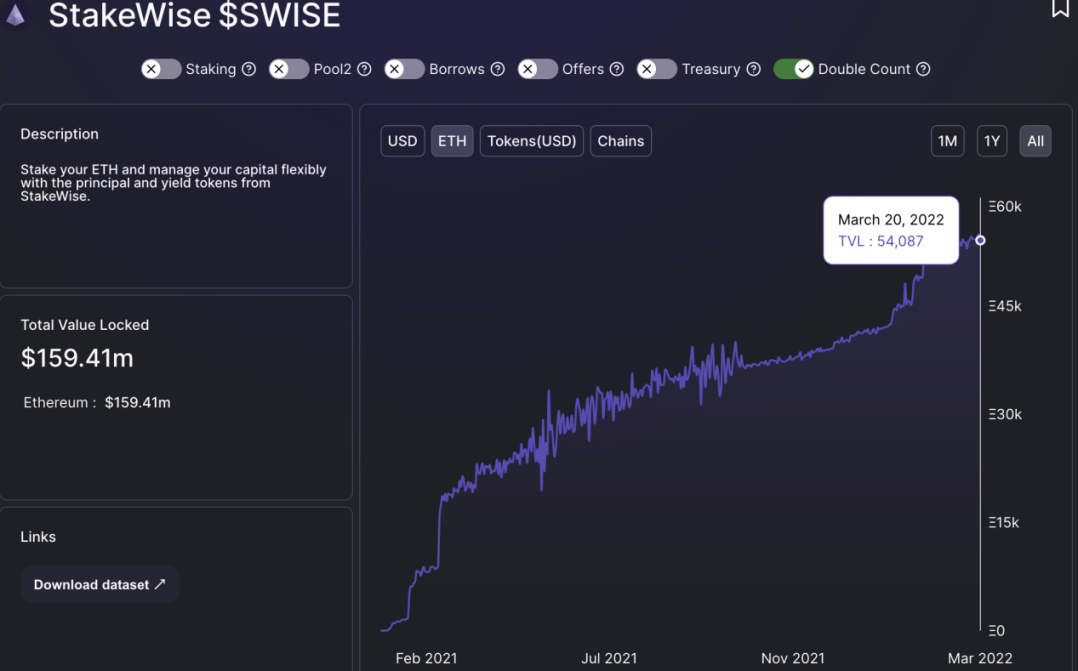
According to DefiLlama data and official website, the current Stakewise TVL is approximately $159.41 million (~54k ETH).
To sum up, the decentralized pledge service solution for ETH2.0 can be roughly divided into two ways: custody and non-custodial. No matter which one is, its development will be closely combined with the establishment and development of ETH2.0. And after the ETH2.0 is officially launched and the transfer is completed, the Tokens and the value of the project replaced by the project will be affected to a certain extent. It is not only the technology and asset management capabilities of the project that need to be observed, but also need to pay attention to its transfer in ETH1.0. 2.0 Operational capabilities in the transfer process.
Like my work? Don't forget to support and clap, let me know that you are with me on the road of creation. Keep this enthusiasm together!

- Author
- More