dark matter.
start:
Dark matter in astronomy and cosmology and theoretical physics is a form of matter that does not participate in electromagnetic interactions and therefore cannot be directly observed. It is about a quarter of the mass-energy of the universe, and only manifests itself in gravitational interactions.

The concept of dark matter is introduced to theoretically explain the hidden mass problem under the influence of abnormally high rotational speed and gravitational lensing effect in the outer regions of galaxies (they involve matter whose mass is much larger than that of ordinary visible matter); among them, it is the most satisfactory.
The composition and properties of dark matter are currently unknown. Within the framework of generally accepted cosmological models, the cold dark matter model is considered the most likely. The most likely candidate to play the role of a dark matter particle is WIMP. Despite active searches, they have not been discovered experimentally.
About Dark Matter Maps
More recently, dark matter maps have been created using artificial intelligence (AI). This detailed map shows previously undiscovered filaments connecting galaxies. Advances in artificial intelligence are helping scientists, and they are using it to create another map of dark matter, this time in a local universe that covers a smaller area.
It's also interesting that creating such an extremely precise map could lead to a new understanding of dark matter and ultimately shed light on the future of our universe. The map contains previously unknown "hidden bridges" connecting galaxies, and also shows previously unknown "bridges" because all galaxies in the local universe are connected into a network. The scientists hope their map, along with their article in the scientific journal Astrophysics, will provide new insights into dark matter and the history of our universe.
Article link: https://iopscience.iop.org/
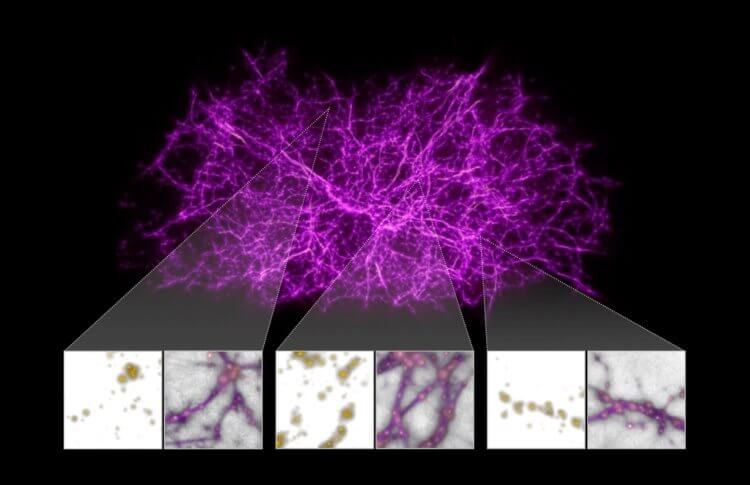
dark matter skeleton
The existence of a mysterious substance that makes up about 85% of all matter in the universe has not been proven today. At the same time, more and more scientists suspect that dark matter does exist. The situation is comparable to the gravitational waves predicted by Albert Einstein, but they were discovered a few years ago.
About A. Einstein:
Albert Einstein was a legendary physicist and a beacon of 20th century science. He was responsible for the creation of general and special relativity, and made strong contributions to the development of other fields of physics. General relativity forms the basis of modern physics, combining space and time to describe nearly all visible cosmological phenomena, including the recognition of the possibility of wormholes, black holes and the fabric of spacetime. The revolutionary physicist used his imagination, not complex mathematics, to come up with his most famous and elegant equations.

The history of dark matter's existence began 106 years ago after the publication of the General Theory of Relativity (GR). Soon after, astronomer Edwin Hubble discovered that galaxies were moving away from Earth (and from each other) at an increasing rate. Over the next few decades, brilliant thinkers such as Niels Bohr, Max Planck, Louis de Broglie, Werner Heisenberg and others worked to create quantum theory.

While it's impossible to observe dark matter directly, it's a generally accepted concept because it doesn't interact electromagnetically with photons. Scientists have drawn many conclusions about the existence and behavior of dark matter by observing its gravitational effects on other space objects.
Cosmologists believe that dark matter acts as the filamentous backbone of the cosmic web, which in turn makes up the large-scale structure of the universe, partly controlling the motion of galaxies and other cosmic systems.
Another daunting task is to directly measure the distribution of dark matter in our local universe, so in the process of working, the astrophysicists used artificial intelligence to create a new map.
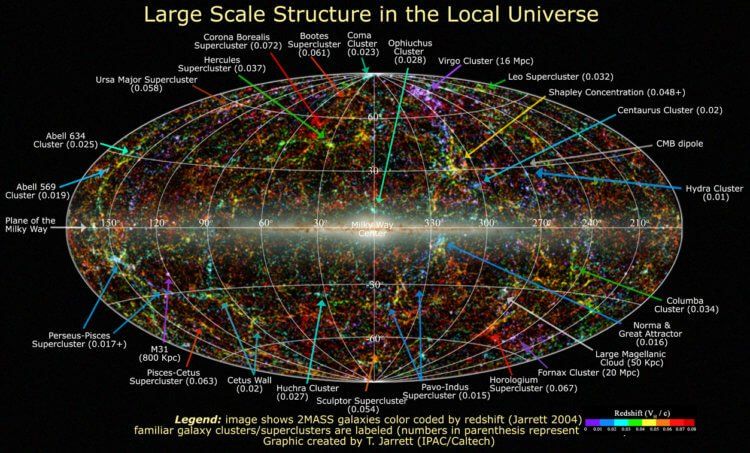
The "local universe" we're also entering is a region about a billion light-years in radius where galaxies and associated space objects are "essentially frozen in their current configuration" and the effects of cosmic evolution are negligible, the astronomers explain .
Donghui Zhong, an assistant professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn and one of the authors of the scientific work, told Big Think that it is much easier to study the distribution of dark matter in the most distant objects, which accurately reflect the very distant past of our universe.
"As the large-scale structure of the universe has grown over time, the complexity of the universe has increased, making it more difficult to measure dark matter locally," the study authors wrote.
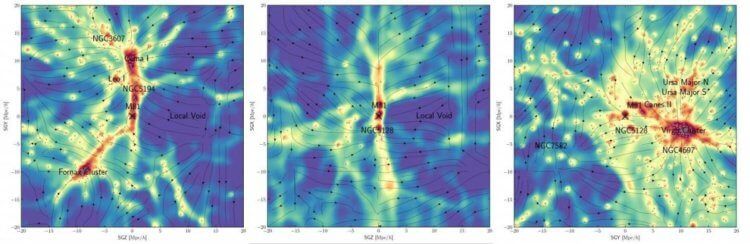
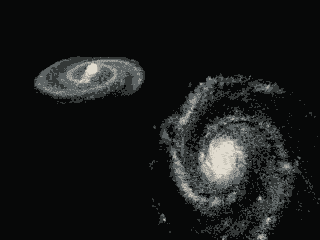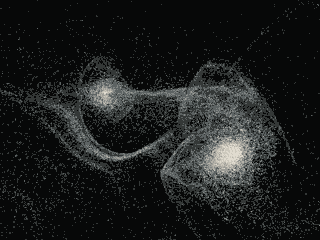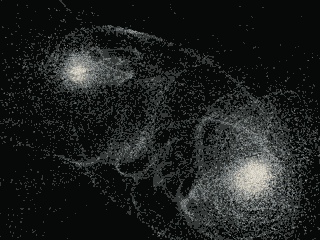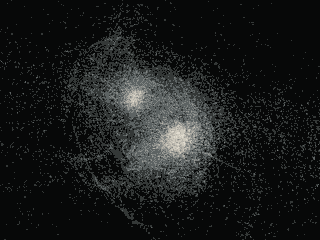
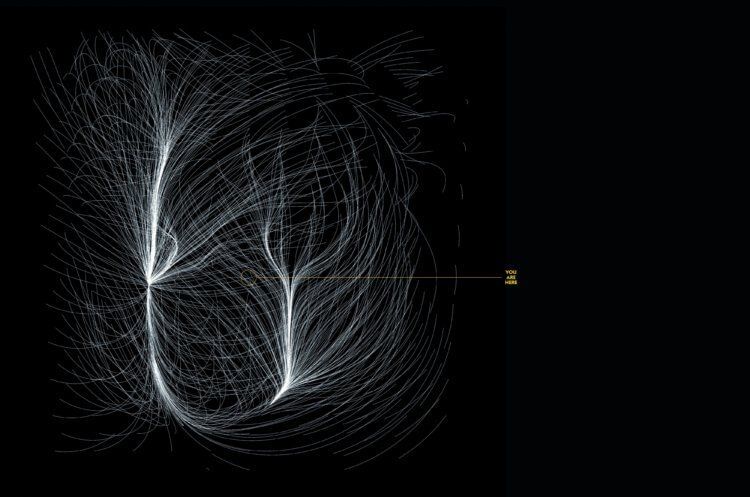
In the image above, smaller linear objects (yellow) act as hidden bridges between galaxies. The gravitational effects of dark matter on galaxies are represented by black dots. The features of the universe are represented by red dots, and the cross marks the Milky Way.
New dark matter map
Therefore, the previously created spatial network map was based on simulating the evolution of the universe 13.8 billion years ago. These efforts require a lot of computation and don't actually provide an accurate idea of the local universe, prompting researchers to develop a new approach.
For the new map, they focused on using machine learning to create models based on the distribution and motion of galaxies. This allowed them to assess how dark matter is distributed.
The AI has been trained to simulate galaxies similar to the Milky Way using Illustris-TNG , an ongoing series of simulations featuring galaxies, dark matter, gas and other matter. As the authors of the scientific paper explained to reporters, if you put specific information into the model, it can rely on already processed data to fill in the gaps. The scientists also confirmed the mapping by applying it to real local data from galaxies in the Cosmicflows-3 catalog, which contains information on the distances of nearly 18,000 galaxies.
Link: https://phys.org/
Hidden Bridge:
The maps the researchers obtained are stunning. Just imagine, for the first time, we can consider the basic structure of the local universe, including the Milky Way. Astrophysicists have also described nearby galaxies and "local voids" -- regions of nearby open space. In addition, the map enables scientists to discover new structures.
In particular, they want to study in more detail the tiny filaments that they discovered seem to link galaxies together. The researchers call them "hidden bridges."
Jeong believes these strands can give us a glimpse into the future of the galaxy. A specific question of concern is whether the Milky Way will eventually collide with the Andromeda galaxy.
"As dark matter dominates the dynamics of the universe, it largely determines our fate," said the study authors.
So astrophysicists can "ask" computers to draw a map billions of years in advance to see what's going on in the local universe. Also, now they can create a new model and travel back in time virtually.
Further research is sure to make our maps more accurate, and the amount of new data from galaxies studied in new astronomy is staggering. Such interesting discoveries await us.
During my work, I used the following materials:
https://ru.wikipedia.org/
https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.3847/1538-4357/abf040
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/05/210525101716.htm
https://elementy.ru/
https://1gai.ru/
https://hi-news.ru/
http://sinp.msu.ru/
Like my work? Don't forget to support and clap, let me know that you are with me on the road of creation. Keep this enthusiasm together!