Revisited: Stanford BIOE 60 ~ Beyond Bitcoin: Applications of Distributed Trust

Dr. Nicolas Kokkalis , founder and technical director of Pi Network, in addition to dealing with any problems encountered in the Pi Network system testing on a daily basis, even if the main chain of Pi Network is expected to be launched at the end of 2021, he will continue to teach blockchain at Stanford University.
Let's relive it together ! On the day of 23/01/2021, everyone saw the course on the homepage of the Pi app. I didn't have time to write an article. I just released it today for your reference and review!
Hi @nicolas, in my Stanford lecture this week, I explain how a blockchain like Bitcoin works. If you want to know the technical mechanics of the classic blockchain, you can watch it on YouTube. I try to simplify the concept
You can watch it in full on Nicolas Kokkalis ' Youtube channel below.
Below is a translation to give you an idea of what Dr. Nicolas Kokkalis said !
How to translate the content of the article Liphardt, J. (PI) Dr. Nicolas Kokkalis Stanford page for information on BIOE 60
Translation_Spoken literal translation, there may be errors

Liphardt, J. (PI):
Good morning everyone and welcome to the second lecture of the Beyond Bitcoin Project. This lecture is the most technical one to date. So please don't be afraid. do not worry. Nicolas Kokkalis and I are here to answer any questions. You can add them to a Zoom or Slack Channel. See you soon!
That way, even if you don't understand them in Nicolas's lecture, you can add us to Slack and we'll be able to answer all of these questions later, with additional documentation. So we explain you here. Nicholas! Are you ready?

Dr. Nicolas Kokkalis
Well, great here are some very quick announcements before we get started.
This year and last year, our class received too many registrations. But the good news is that, starting this year, the lectures are broadcast via video and we are able to invite judges. So, starting today, top-notch judges are also participating via Zoom. That's why you see a lot more people in the room today than last time, and the next two tech classes are likely to be in class. This is an original lecture for a computer science class I designed.
But don't worry, it's been tweaked a lot. It's simplified, sometimes to the point that no basic knowledge is required. We wanted these two lectures even though they seemed a little too technical to many students, or because there was so much going on behind Bitcoin.
This makes it sound complicated. In fact, it's actually quite a simple concept. All these puzzling puzzles need to be solved. All of these concepts may sound strange at times, but they are actually quite simple. If we tell you exactly what they're talking about, I'd like to provide you with a work plan for today and the next class. If we have time, we will discuss the following 5 topics and possibly some advanced topics. Therefore, the hash topic is a very important platform needed to build a block chain. What are we going to talk about? Then, what will become the blockchain.
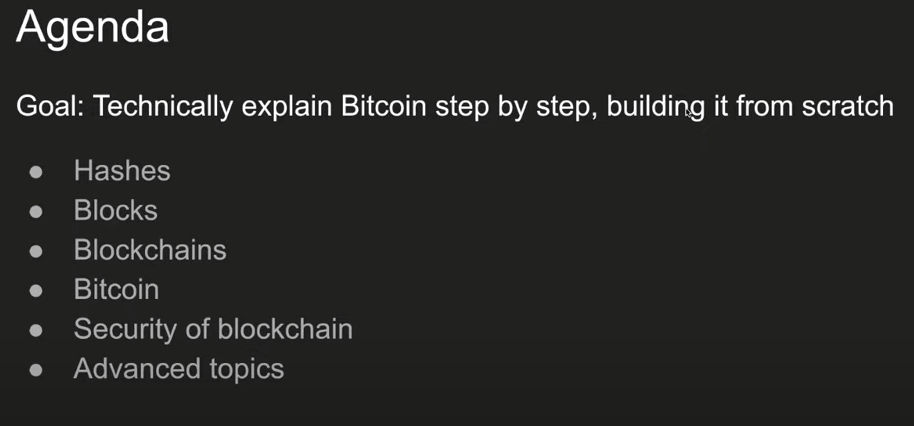
Then, we'll discuss how Bitcoin ties these concepts together, and then most likely in the next lecture, we'll discuss blockchain security and Bitcoin security. Why can we have anonymous miners or nodes as their other way of calling them people who process transactions and we still trust them? This is entirely possible because of the cryptographic properties used by Bitcoin and blockchain. So without further delay, let's start with the simplest thing, a hash is a function, just like in math. As a function, it gives us an input, which is data of arbitrary length. It can be a text file.

It can be a block in the blockchain and as output it creates a digest of that data to a specific size. what do i mean? This is stuff, assuming what looks like a string is always the same, the same size. So data can be a subpoint no matter how big it is. That hash size is still the same. The data can be, the whole giant video file is still the same size, take the data and create half of it.
One of the important properties is that the same data always results in the same hash. This feature is so popular that Bitcoin uses, it's called SHA256. It's 256 because the result has 256 bits. If you convert it to decimal, you get 64 bits. Here's why, here's how to interpret it. Let me show you a concrete example. So, if I click here, it will open that this software is open source software, and I used a little bit for the purpose of today's talk so that it can emphasize the point I want to make.
I will point to the link to the source code.
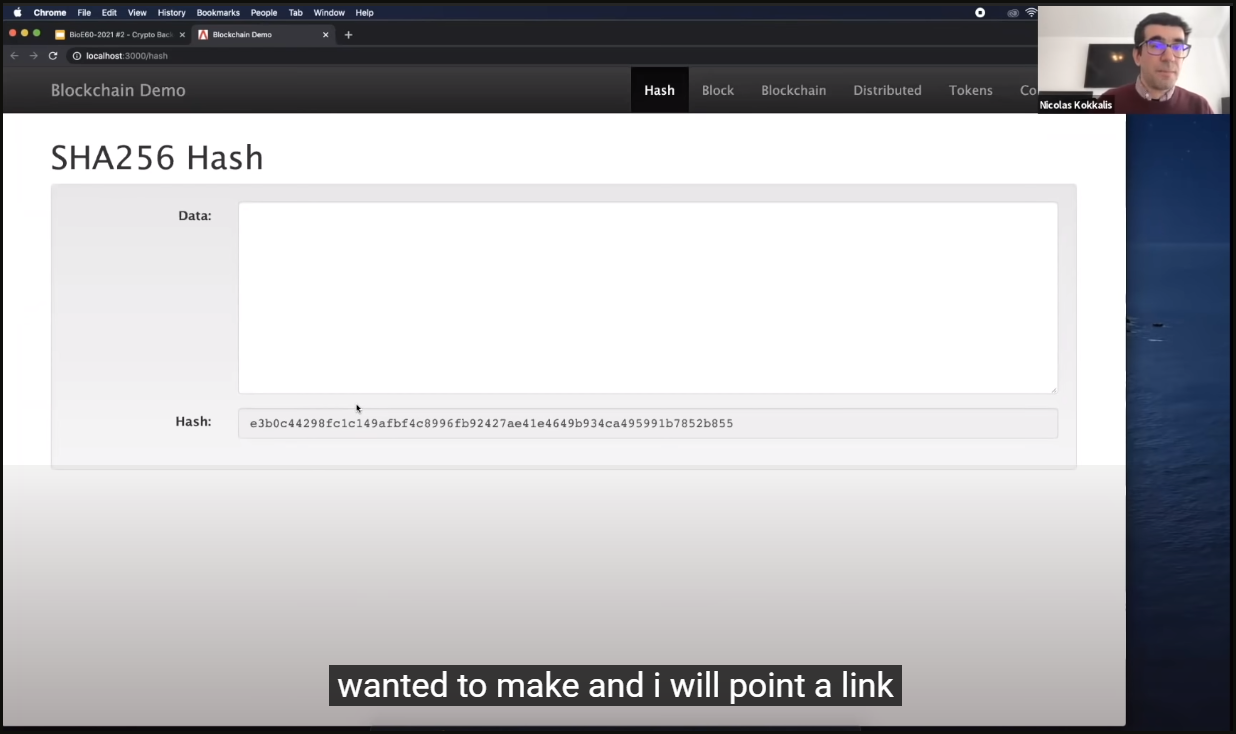
I don't write software just to modify it. So this is an example, but I like it because it's very intuitive. If I set the data to character A, I get the hash here. If I change this to AB, the result has changed significantly, the whole hash is completely different. Although my input is only individual characters. I don't see any character changes in the hash I've seen.
This completely changes. Let's go back to A and see that the hash is still the same. You see A has a hash of 559, and adding B, back to A is still digits 55 and 9, no matter what I do. As I said, the data may be of arbitrary length. Well, it can be very long, the hash is the same size. Well, there is now an opinion that certain hashes are safe. This will be the subject of the next lecture, where I will explain to you why and why this is important. How safe are they? But this feature makes blockchain basically feasible. But we're not there yet. Now, let's talk about blocks. To talk about blocks, I'm going to start talking a little bit about finance, the ledger. So let us introduce you to your finance course.
Ledgers are basically spreadsheets or financial transactions and why are we talking about ledgers. This is the foundation, the foundation of blockchain is basically a ledger, a decentralized ledger. So that's why we're talking about the ledger now and explaining the reference. So here is a ledger that looks like this. Here is a list of financial transactions. Alice gives Bob $1 at 5:00pm, Bob gives Bob $0.50 at 5:00pm...their transactions have a schedule.

Well, now for some reason there is no explanation as to why, instead I think in short we have a lower quality ledger here. Rather than storing the exact time each transaction happened, we'll store the transaction every 10 minutes, so if we lose this information when the transaction actually happens, we'll be fine. Well, well if we start hosting at 5:10. get me back, we're at 5:10

We have information about these three transactions, so we can simply store them at 5:10 as if they all happened a few minutes later, also at 5:20. We have this deal at 5:30. Now this concept goes a step further, let's say, all the transactions here are 5:10 and they all happen at 5:10. I don't need to store at 5:10 at a time. Suffice it to say, it all happened at 5:10, after 5:20, it all happened at 5:30.
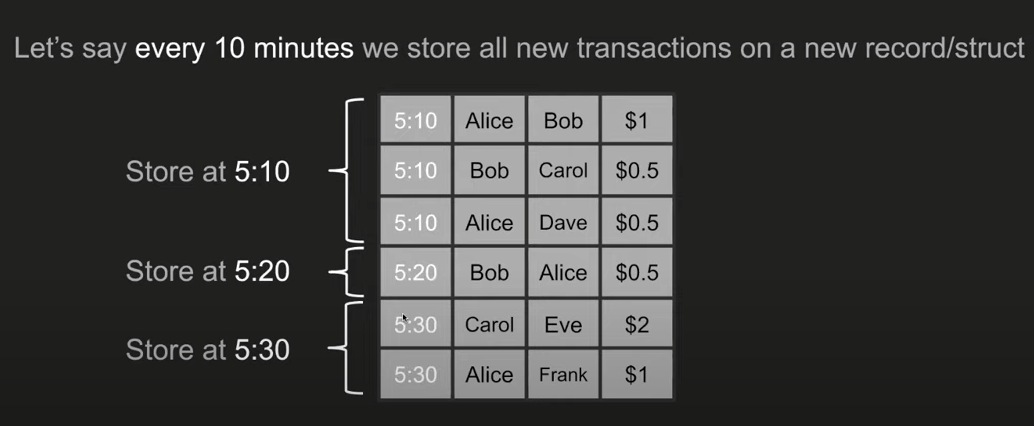
So I went ahead and created computer science concepts there. So for some reason I just need to separate my transactions into different records, I call record 1, record 2 and record 3.
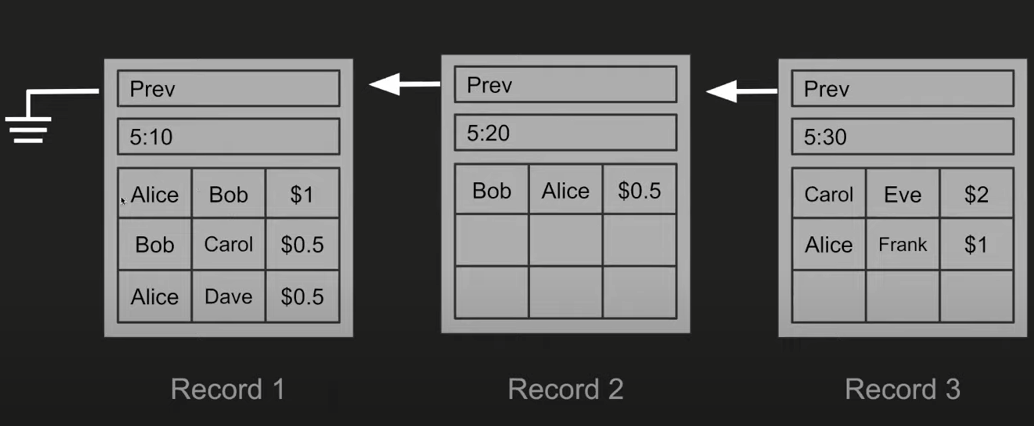
Instead of storing in one big spreadsheet, spread each record. Assuming it's a different spreadsheet, every 10 minutes I have a new spreadsheet. Now I want to keep track of the order of the spreadsheet. I can store this information, tell me, and it gives me a link, like a google spreadsheet. Google Spreadsheets gave me a link to preview the spreadsheet so I can store receipts ahead of time. This is how I find all previous spreadsheets, follow these cursors, there will obviously be an original record, which will be the first
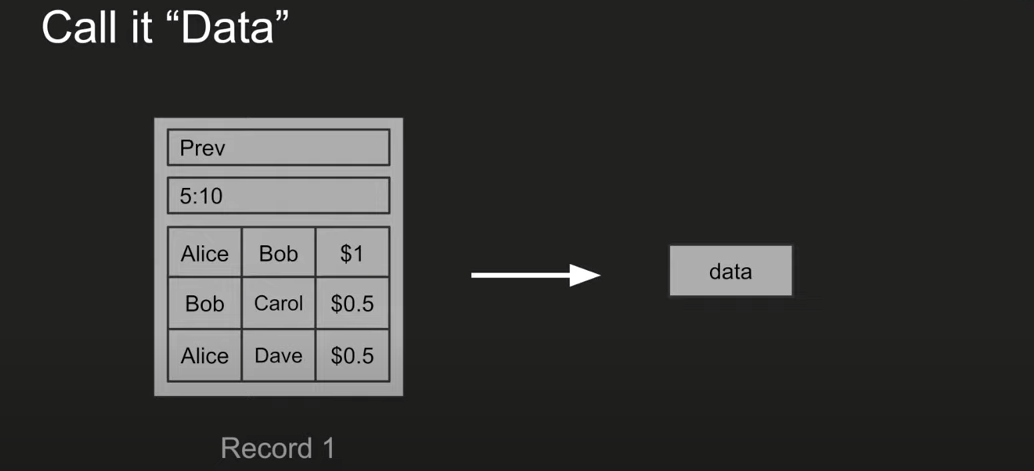
Ok, now let's try to abstract the concept further, let's call all this data, because I'm trying to convey to tell you what blocks are, and simplify them. I just call all the content data, then a blockchain block, and more, but what the heck is it. Data is said, we call it nothing and a hash combines data with nothing, these three things. What is it now? Just an arbitrary incompetence, number it, I can change anything I want, it doesn't really change anything I store in this block, because the transaction is completely independent of the data and the non. But, it's very important because the reason I have it is that when I change the nobody, although the data stays the same, the transaction between us stays the same, so the hash of this block changes. So now Bitcoin or Ash has come up with this, saying a valid block is a block where the hash starts with multiple 0s. Consider for a minute, in a few examples. But hashes usually don't start with more than one digit 0. Hash because I showed you before.
This is the end of the translation for now, check out the original video about the lecture for more information!
Information on BIOE 60 on Stanford page
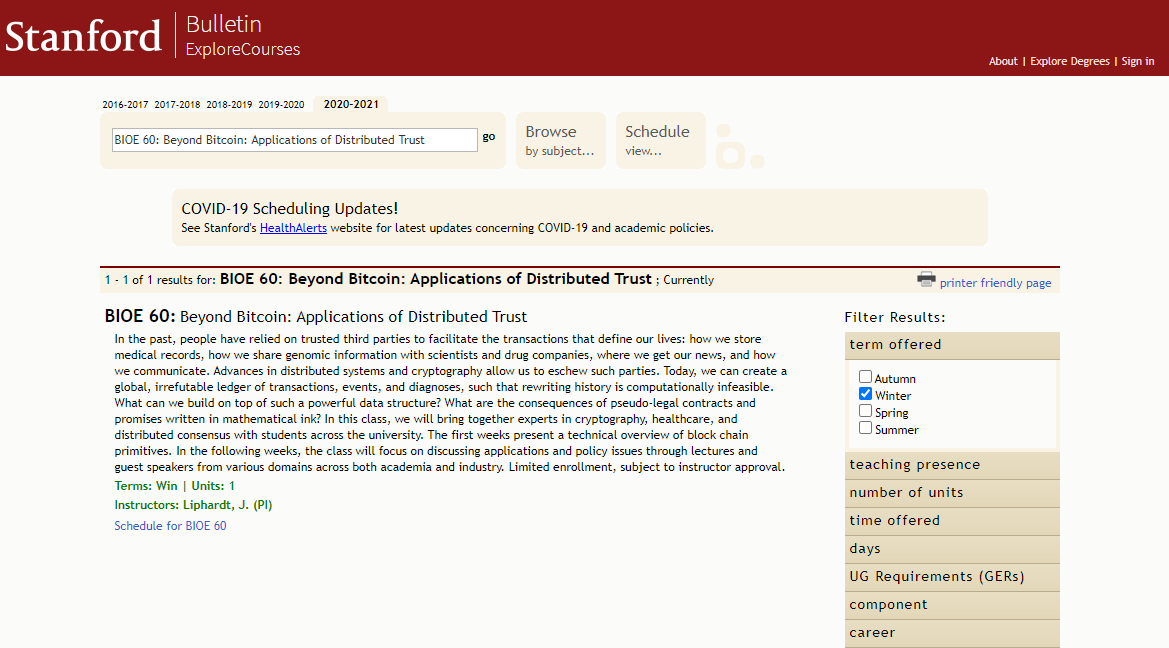
BIOE 60: Beyond Bitcoin: Applications of Distributed Trust.
In the past, people have relied on trusted third parties to facilitate the transactions that define our lives: how we store medical records, how we share genomic information with scientists and pharmaceutical companies, where we get news, and how we communicate. Advances in distributed systems and cryptography allow us to avoid these parties. Today, we can create a global, irrefutable ledger of transactions, events, and diagnostics such that rewriting history is computationally infeasible. What can we build on top of such a powerful data structure? What are the consequences of bogus legal contracts and promises written in mathematical ink? In this class, we will bring together experts in cryptography, healthcare, and distributed consensus with students from across the school. A technical overview of blockchain primitives is presented in the first few weeks. Over the next few weeks, the class will focus on applied and policy issues through lectures and guest presentations from various fields in academia and industry. Enrollment is limited and subject to faculty approval.
Teaching Professor: Liphardt, J. (PI)
Pi Network founder and technical lead Dr. Nicolas Kokkalis has long believed in the technical, financial and social potential of cryptocurrencies, but is frustrated by its current limitations. And is committed to bringing the power of blockchain to more people, improving the current experience, and creating value for everyone.
So he turned the development process of new blockchains upside down by adopting a user-centric design philosophy. Released in the beta version, members are invited to join the network, and the protocol is iterated with members to decentralize the design results.
Dr Nicolas Kokkalis said: “The current result is Pi Network, a new currency and peer-to-peer network that is currently operating in over 150 countries and 30 languages. Pi Network is 100% of my professional commitment, and my My beloved wife and son take 100% of my personal commitment."
If you haven't joined Pi Network yet, join now! Create a blockchain project that belongs to everyone with us!

The Pi app can be searched in the Android PlayStore or Apple's App Store: PI NETWORK, free download , or download the Invitation code from the following link: kyle2051
iOS: https://apps.apple.com/us/app/pi-network/id1445472541
Android : https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=com.blockchainvault
If you need a code, enter kyle2051 (use this code after day 4 for a 25% speedup)
Tip: You don't need to keep the Pi app open, the Pi won't affect phone performance or drain battery power or use network data. You can even close the app after pressing the lightning button and you'll keep mining the Pi. The mining of Pi will stop every 24 hours, press the ⚡️ lightning button once again, repeat every day until the end of the distribution
Pi Network official website : https://minepi.com/
Data Privacy : socialchain.app/privacy
Terms of Service Last Update Posted: August 25, 2020 SocialChain
If you enable in-app money transfers in our mobile app, you also agree to the following additional terms and conditions. You agree that you will not offer any sale of Pi or any derivatives of such units (such as "futures") in other currencies prior to the launch of the Pi Network mainnet. You agree that you and only you are the sole holder of the account and the Pi units associated with your account and that you will not transfer your account to other individuals, groups or organizations. You agree not to engage in any illegal and/or illegal Pi transactions.
Violation of these terms may void your account and cancel your entire balance , including any Pi units transferred from your account. You agree that in the event of invalidation of your account and cancellation of your Pi balance, you will be solely responsible for the invalidation of your account , cancellation of your balance , or cancellation of any transferred Pi units, SocialChain, Pi Network and its development does not assume any responsibility.
Like my work? Don't forget to support and clap, let me know that you are with me on the road of creation. Keep this enthusiasm together!


- Author
- More