
人类迷惑行为观察员
【Web3 Study Notes】#2 Decentralized X: Reasons and Applications of Decentralization
In this week's learning sharing meeting, Liu Guo introduced the evolution of decentralized technology from the perspective of technical architecture . At the end of the article, he quoted the decentralized classification proposed by Vitalik Buterin , which was discussed based on computer networks and software. Interested friends Please read his original text. The following is my personal interpretation, not a complete and accurate translation:
- Logical decentralization : Can the interface and data structure of a software system be flexibly assembled? If a system is cut in half, can the separate parts still function independently? Insert a cold knowledge: Modern medical research has found that if a part of the human brain is removed, the remaining part can still slowly learn to lose the function of that part of the brain, especially if the person is still a child and the brain is still vigorously developing (high level of neuro plasticity), the person can restore almost full brain function. Even if you're an adult, studies have found that you can still regain some function with consistent training. Neuro plasticity is hope for Alzheimer's disease. This phenomenon originally belonged to the field of Neuroscience and greatly inspired the design of computer networks.
- Architectural decentralization in computer architecture : In a computer network, if there is a central server in charge of all the logic and task distribution of the network, then as long as a hacker attacks the central server (or a natural disaster causes the server to fail), the entire network will be destroyed. The system will be paralyzed. In terms of business value, this is the incentive for enterprise software to move to distributed computing networks. However, the cost of deploying application software to a distributed network is to invest a higher cost to ensure information confidentiality, which is a big challenge for traditional banking and insurance industries, which is why they are moving towards distributed Be more cautious on the way to the network.
- Political decentralization in political decision-making : Is the power to make decisions only in the hands of a few people? If not, how should the decision be made? If no one in this network has the power to judge impartially, how can we ensure that a few collaborators do not join forces to extract the collective benefit?
It should be pointed out that how this computer network is structured and how the logic is designed will ultimately affect the decentralization of political decision-making, so in fact, these three categories of "decentralization" are interactive and related to each other. It may be discussed out of the limitations of the technical framework. The organization, collaboration and possible incentive mechanism of the DAO community shared by Jieping - a group of people gathered together, not only can invest together, share accounts together, but also work together to complete complex tasks, in fact, it is at the level of political decision-making question. In my study notes last week , I used the analogy of ride-hailing, referring to the pull between participants and the platform :
Decentralized management does not mean decentralized profit distribution .
At this point, the metaphor of car-hailing is no longer suitable for exploring the DAO model, because the original intention of the car-hailing platform is not to better distribute profits to platform participants, but to make profits for the platform itself. Recently I read an article about applying DAO logic to scientific research and knowledge sharing , which is worth thinking about. The following are excerpts of the main points; the following focuses on the pattern of profit distribution.
Scientist's Problem
According to Sarah Hamburg, the author of the article, the main problems faced by scientific researchers are: research needs funds, and the institutions that provide these funds are often either the government or large enterprises; the government and enterprises have their own interests, which may force researchers Doing things that go against the spirit of science: from being held back by bureaucracy that makes it difficult to collaborate across disciplines/regions, or being asked to cover up or tamper with data.
Not only that, but researchers spend almost half their working time applying for grants. The process of applying for funding is not only time-consuming and labor-intensive, but success also depends on whether the funding agency recognizes the value of your project. As a result, many basic research and public projects are not funded.
At the same time, scientific knowledge is often hidden in scientific journals and requires payment to read. A decade ago, the Open Science movement arose in the scientific community and led to regulations by the US National Health Service requiring publishers to open access to information. However, journals have responded by charging readers who want to publish, since they can’t charge readers. Those researchers who have insufficient research funds are also facing the crisis of research results but no money to publish.
This is where DeSci came into being; this round of movement has seen (1) making research articles into NFT auctions (2) the emergence of various research DAOs (3) individual scientists issuing tokens to crowdfund R&D projects.
Blockchain related technical support and application in DeSci movement
(Most of the application prospects mentioned below are still in the proposal stage and need to be further demonstrated and implemented)
Reward Peer Reviewers with Smart Contract
Every academic paper must go through peer review before publication; researchers in the same field do not get paid to review each other's papers, while academic journals can earn considerable intermediary fees. Using the smart contract on the blockchain allows authors to connect directly with reviewers, eliminating the need for journal intermediaries; and reviewers can get NFT or token rewards.
Verify the credibility of scientific researchers with the holding of relevant tokens or NFTs
At present, the credibility of researchers comes only from the academic papers they publish. Using blockchain, they can make their other work, including peer review, teaching, publishing experimental data for other researchers to use, etc., are rewarded with tokens or NFTs - these tokens/NFTs are not necessarily worth much cash, but It can be used as a credential for scientific research. Even students who are still working under the tutor's name can build their credibility by doing data sorting, writing basic analysis, etc.
Crowdfunding Research Funding
So what's the difference between blockchain-based crowdfunding and the web2 crowdfunding we've already seen?
The original author of this question, Sarah Hamburg, did not explain in detail, but I am very interested. Following the link she provided, I searched around, and here are a few new funding models that I feel are more reliable:
💰 Quadratic Funding
In fact, I don't understand this mathematical formula, but I feel that it can provide a little fairness to the distribution of funds for non-profit projects, avoiding the situation that whoever pays more listens to whoever. Let's enjoy:
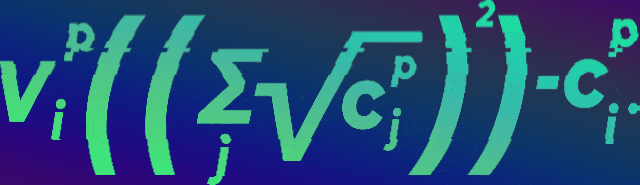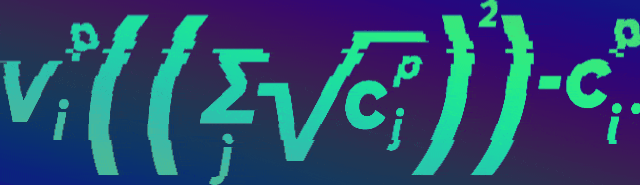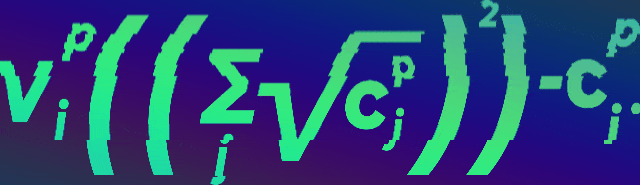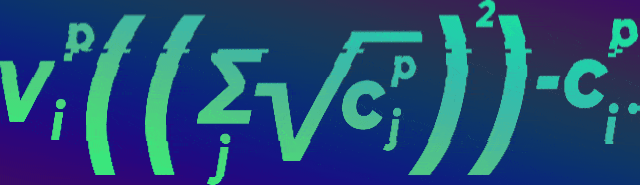
This ignorant formula is actually very clear and simple by looking at the following model. Suppose there are four proposed projects applying for funding, and a wealthy institution says, I have 1,000 yuan to invest, but please help me identify these projects, which projects are more worthy of funding? Suppose there are fellow scientists in this community. According to the token=reputation model mentioned above, everyone has a certain token that can be used to vote.
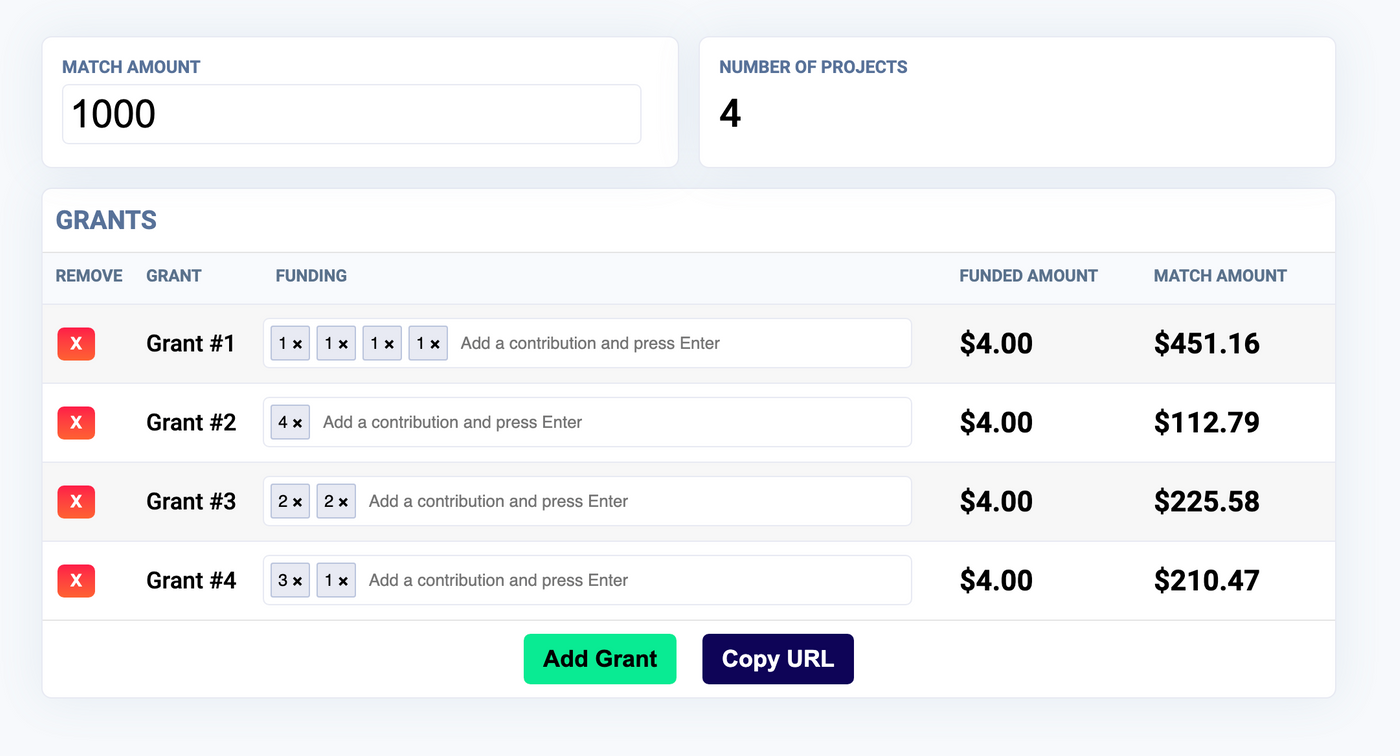
As shown in the figure, the first project got four scientists each 1 token (represented by $1); the second project one scientist gave $4; the third project, 2 bits x $2; the fourth project, 2 bits, $3 + $1. Although all four projects received a combined $4 of scientists' votes, the first project received $451.16 of the funding agency's $1,000 because it cared the most. Several other projects received less funding. This interactive program is on the WTF is Quadratic Funding website, and you can try it out by entering the numbers yourself.
💰 Utilize NFT's rewarding properties to fund further R&D
NFTs can provide royalties-like benefits. If your scientific research results are published as an NFT, then when the NFT is forwarded and cited, you can get a commission; so you don't have to be under pressure to publish how many papers every year. A widely circulated strength paper can earn you consistent income. Of course, this is just a beautiful dream, and the technical realization is still far from it.
💰 Retroactive Funding
It's also mentioned in this Jieping sharing, It's easier to agree on what was useful than what will be useful. Regarding this, V God wrote a very detailed idea , I vomited blood after reading it (not fully understood), No excerpts and translations 🤪.
💰 DeFi model supports long-term funding (similar to tenured professor system)
The term DeFi is too broad, and I will write a separate article in the future. Here, if you want to devote yourself to basic research and not worry about your livelihood, the only way out is to enter a reputable university research institute and strive to be hired as a tenured professor. Such opportunities are of course very limited, and hiring decisions are in the hands of a handful of well-funded institutes. If there is a way of decentralized capital operation to provide basic salary guarantee for those reputable researchers, more people can participate in basic research.
. . .
In addition to the three points I highlighted above, the original author Sarah Hamburg also mentioned other applications, including forming DAO communities with disciplines or related topics, and motivating the community to do paper curation and peer review; and persistent storage experiments Data to combat political interference, etc., will not be repeated here.
Of course, DeSci itself has many challenges to face, and Sarah Hamburg cites many. My main concern here is: Whose interests will DeSci ultimately serve? The scientific research community wants to decentralize. Originally, the "centers" they wanted to resist were scientific research funding agencies and academic journals, but the new order created by blockchain-related technologies, Is it possible to avoid the concentration of power in the hands of a few again? Can the scientific research community return to its original aspiration of social ideals and serve education, medicine, academic exchanges... ? After all, in a commercial operation, it is easier for those who have accumulated wealth and fame to gain continuous exposure and support.
De(Whatever) has become so popular, I think it should reflect the general distrust of the central power, and the realization that networks that rely too much on the "central" (including computer networks, communities, ecological networks...) are more likely to be paralyzed . But DeX isn't the answer to all questions. When considering setting up a DeX, you still have to think about what problem this thing is going to solve. In the process of writing this study note series, I also kept asking myself: what attracted me? What do I want to achieve?
See you next week.
Like my work?
Don't forget to support or like, so I know you are with me..
Comment…